Resolve AR or AP on the cash basis Balance Sheet with journal entries
by Intuit•7• Updated 1 year ago
Cash basis financial reports should not display Accounts Receivable (A/R) or Accounts Payable (A/P) balances. However, QuickBooks is a bookkeeping program and must balance, so for accrual-based business that reports on cash basis, QuickBooks will display AR and AP.
This article provides steps to take when A/R or A/P balances show on your Cash Basis Balance Sheet (CBBS) report and you need to remove them. Specifically, it describes:
- How to create a General Journal Entry to remove AR and or AP balances from a cash basis balance sheet on the last day of a reporting period.
- How to reverse the General Journal Entry on the first day of the next reporting period.
Remove Accounts Receivable
- Create a journal entry to remove A/R from the CBBS on the last day of a reporting period.
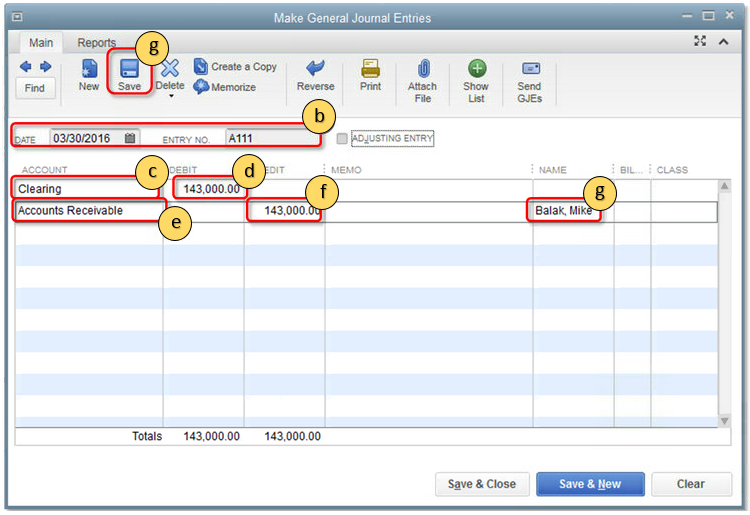
- From the QuickBooks Company menu, select Make General Journal Entries.
- Enter the Date and the Entry No.
- On the first line, select the Account column, then select an appropriate offset account. Note that the offset account must be an account other than Accounts Receivable and will often be an Income or Asset account. Consult with your accountant if you are unsure which account to use.
- In the Debit column, enter the amount.
- Go to the second line and in the Account column, select Accounts Receivable.
- In the Credit column, enter the amount.
- In the Name column, enter (Quick Add) an AR Adjustment Customer Name, then select Save.IMPORTANT: This is required if you use A/R or A/P accounts.
- Create a reversing entry on the first day of the next reporting period.
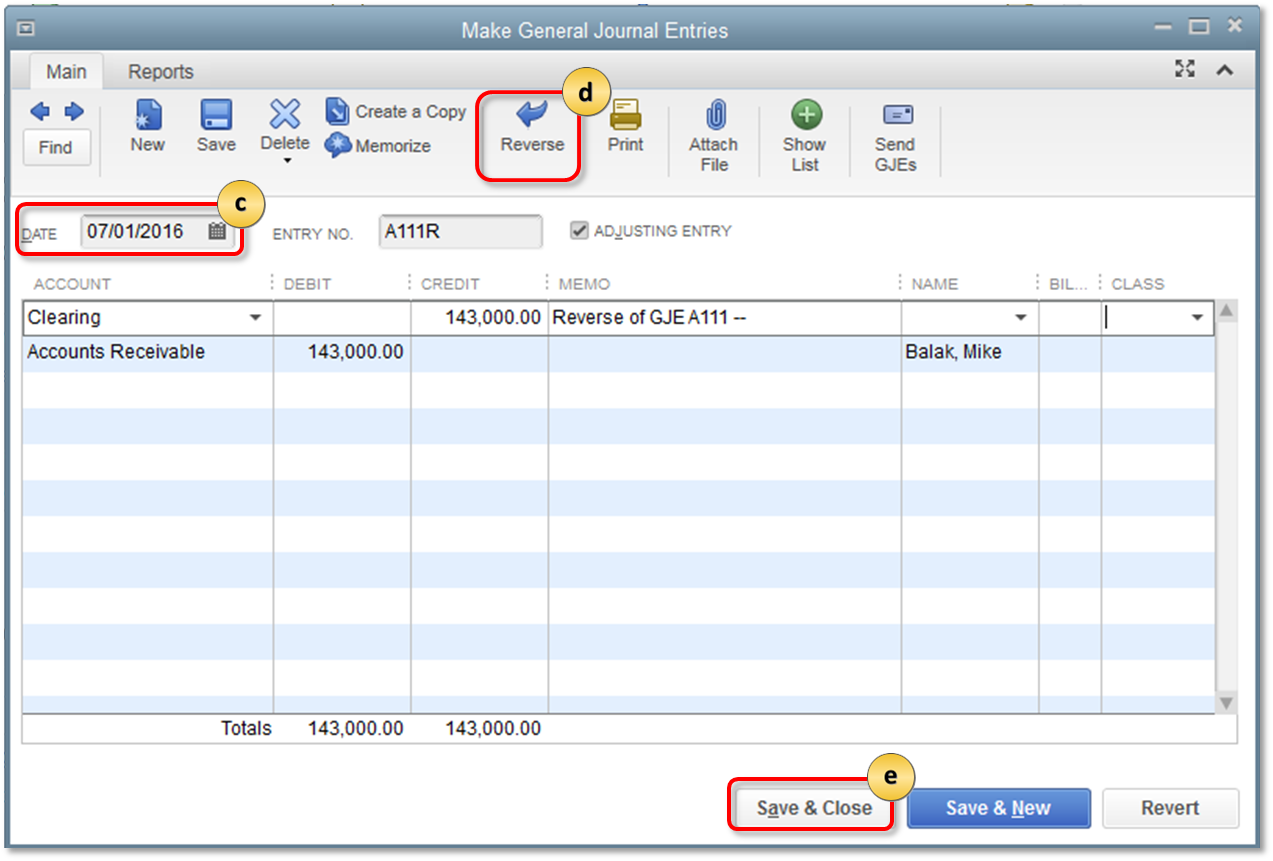
- From the QuickBooks Company menu, select Make General Journal Entries.
- Find the journal entry you created in step 1.
- Change the date to the first day of the next quarter, if prompted to save changes, select No.
- Select Reverse on the top of the Journal Entry window.
- Select Save & Close.
Remove Accounts Payable
- Create a journal entry to remove A/P from the CBBS on the last day of a reporting period.
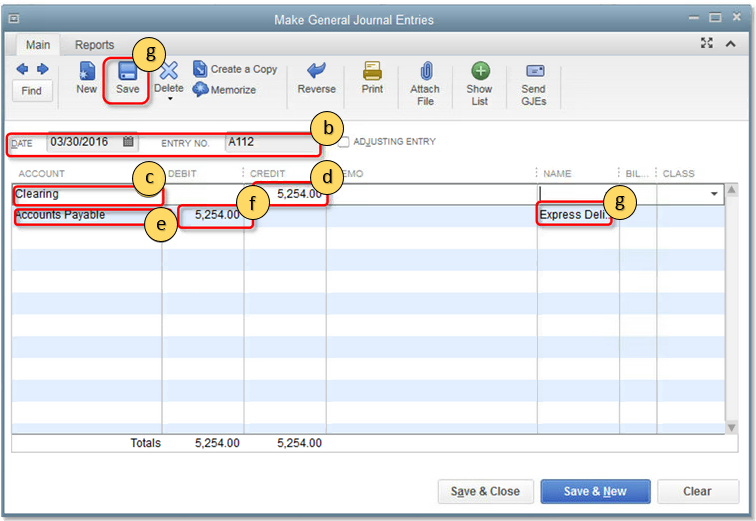
- From the QuickBooks Company menu, select Make General Journal Entries.
- Enter the Date and the Entry No.
- On the first line, select the Account column, then select an appropriate offset account. Note that the offset account must be an account other than Accounts Payable and will often be an Expense or Liability account. Consult with your accountant if you are unsure which account to use.
- In the Credit column, enter the amount.
- Go to the second line and in the Account column, select Accounts Payable.
- In the Debit column, enter the amount.
- In the Name column, enter (Quick Add) an AP Adjustment Vendor Name, then select Save.IMPORTANT: This is required if you use A/R or A/P accounts.
- Create a reversing entry on the first day of the next reporting period.
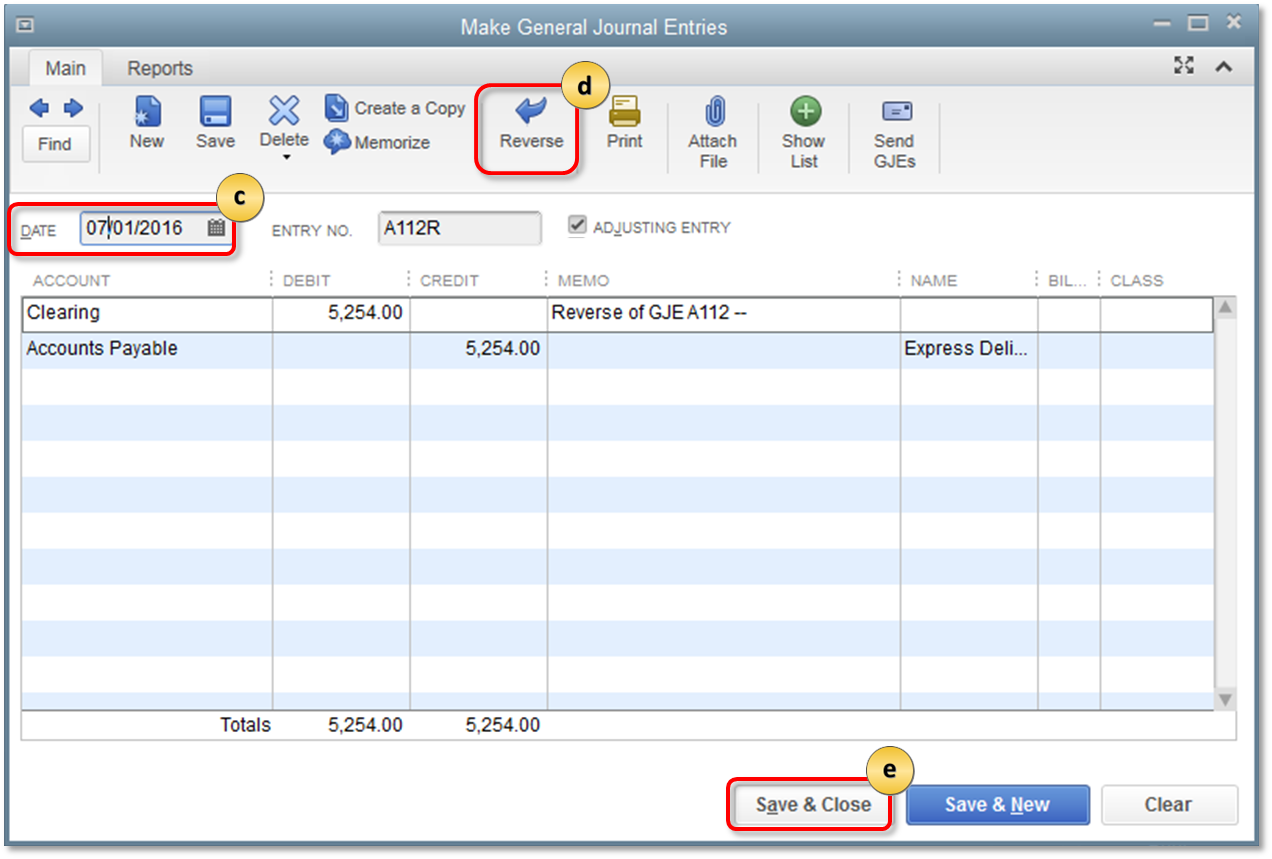
- From the QuickBooks Company menu, select Make General Journal Entries.
- Find the journal entry you created in step 1.
- Change the date to the first day of the next quarter, if prompted to save changes, select No.
- Select Reverse on the top of the Journal Entry window.
- Select Save & Close.
QuickBooks requires a name whenever A/R or A/P account is used in journal entries or transactions - primarily, so it can generate A/R and A/P reports correctly and ensure that the totals of these transactions match those of the main A/R and A/P accounts.
The solutions outlined in this article are generally not covered by CCP. If the customer doesn't have an active support plan, be sure to provide them with a solid roadmap and the best support option before you start troubleshooting. To learn more, refer to our software support policies (US or CA).
More like this
- Resolve accounts receivable or accounts payable balances on a cash basis balance sheet in QuickBooks Onlineby QuickBooks
- Differentiate Cash and Accrual basisby QuickBooks
- What transactions are not supported by Balance Sheet by Class in QuickBooks Desktop?by QuickBooks
- Resolve accounts receivable and accounts payable balances on a cash basis balance sheetby QuickBooks