Defining accounting ledgers
An accounting ledger is part of the bookkeeping system and is used by businesses to record all their financial transactions. Businesses will create separate categories for such transactions, which are known as accounts. All account records of a company will be listed and contained within the general ledger, or principal book of accounts.
What does a general ledger include?
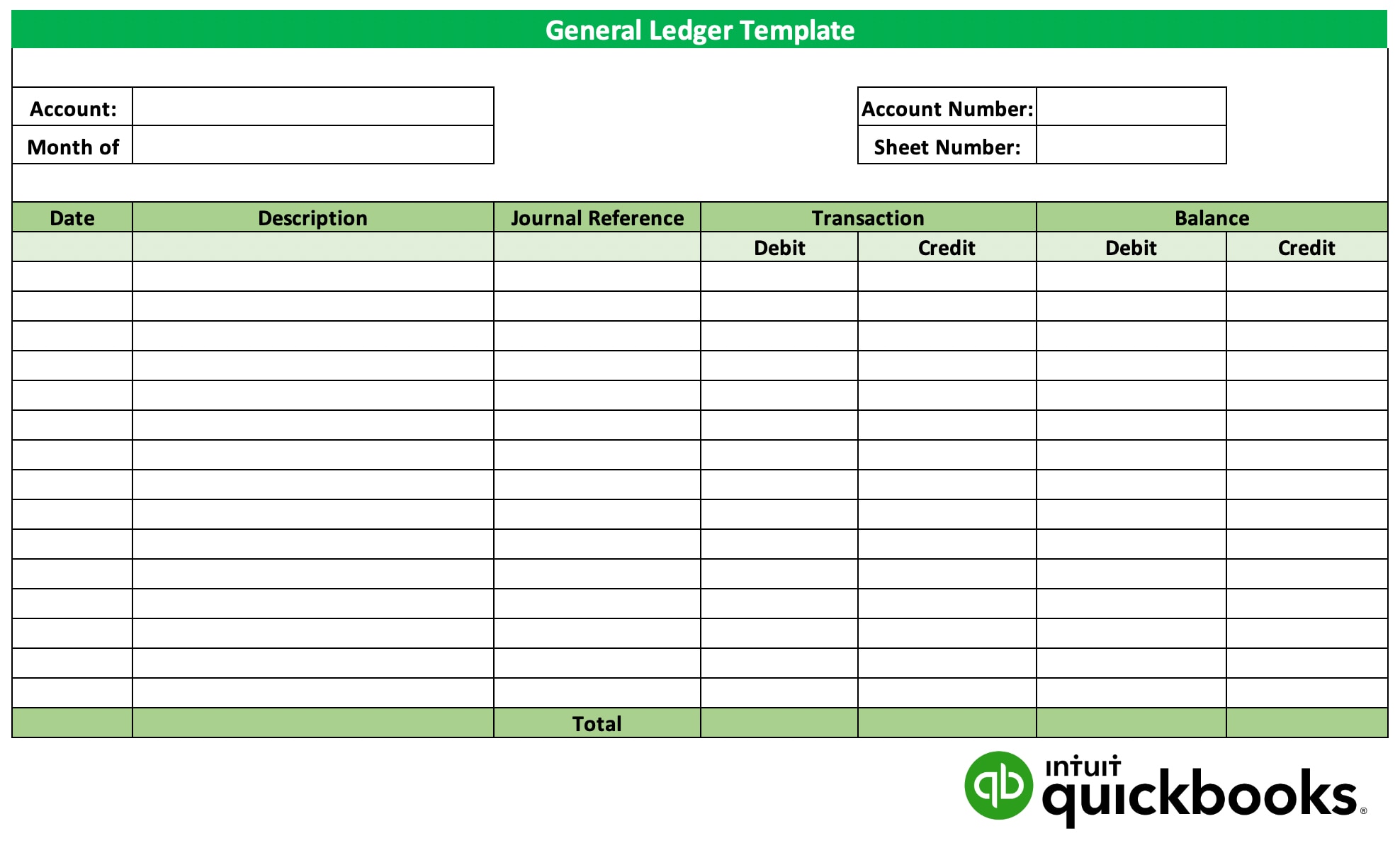
A general ledger has four primary components, these include a journal entry, a description, debit and credit columns, and a balance.
- A journal entry: The number of each journal entry posted to the account and the date of the entry.
- A description: A description of the transaction.
- Debit and credit columns: Each journal entry posts a debit or credit to the general ledger.
- A balance: A general ledger lists the account balance each time a debit or credit posts to the account. At months-end, after all the journal entries post, the ending balance is calculated.
You can use the account balances in the general ledger to generate the trial balance, which lists every account and the current account balance. The dollar amount of total debits must equal total credits in the double-entry accounting system.
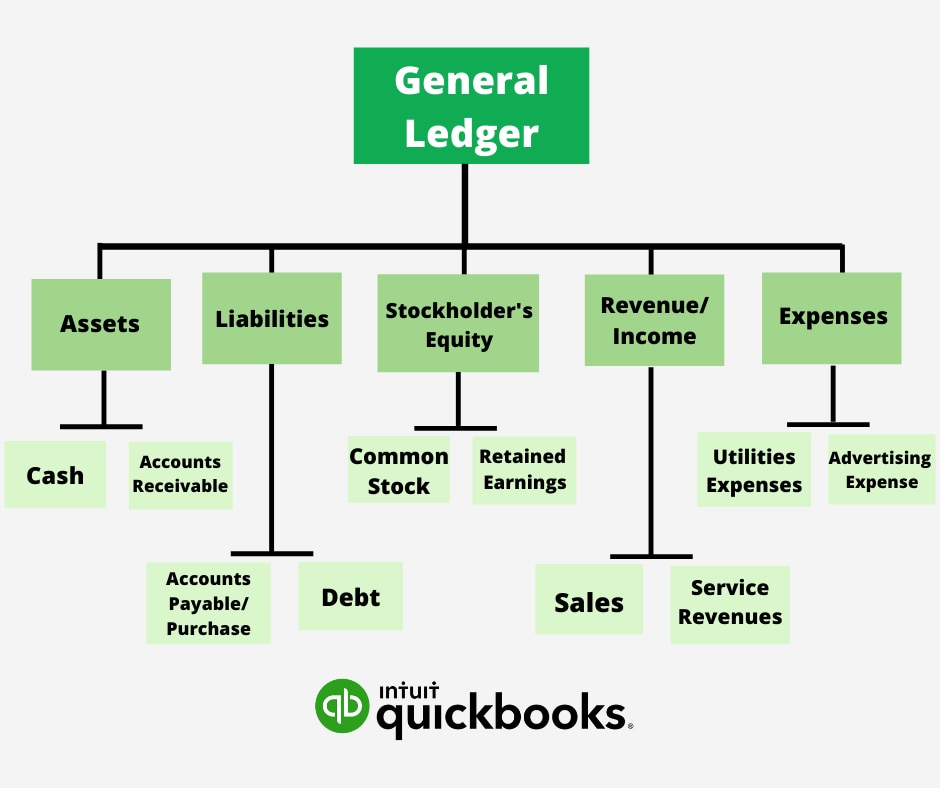
The general ledger must include all accounts of a business that will appear on their financial statements at the end of an accounting period. These are known as general ledger accounts or GL accounts.
The five key type of GL accounts are:
- Assets
- Liabilities
- Equity
- Revenue/Income
- Expenses