Gross vs. Net Income
Gross and net income have different meanings, depending on whether it concerns a business or a wage earner. Net income for individuals is the take-home pay you have received from your endeavors.
In terms of a business, gross income, as mentioned before, is the amount your business earns from selling goods or services before tax, administrative, selling, and other expenses are deducted.
Alternatively, net income is the residual amount of your company’s earnings after deducting all sales expenses. Gross income is the intermediate earnings figure before your costs are included. In contrast, net income is the final profit or loss after your costs are included.
Their formulas are as follows:
Gross Income = Revenue - COGS.
Net Income = Gross Earnings - Expenses.
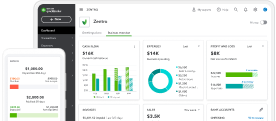
For example, let’s say your business has sales of $1,000,000. Your cost of goods sold is $600,000, and your selling expenses are $250,000. Your gross income will then amount to $400,000, and your net income will be $150,000.
In your income statement, you will notice it shows revenue and cost of goods sold. Your gross earnings will follow this. Net income is the bottom-line item of your balance sheet and is typically revealed after the other expenses.
If your company’s net income is less than your gross income, you will need to cut other expenses, such as your indirect costs. Unlike gross earnings, net income recognises other incomes such as dividend income and interest income.