Industry newcomers tend to use the terms “bookkeeper” and “accountant” interchangeably, but there are a few important distinctions between the two.
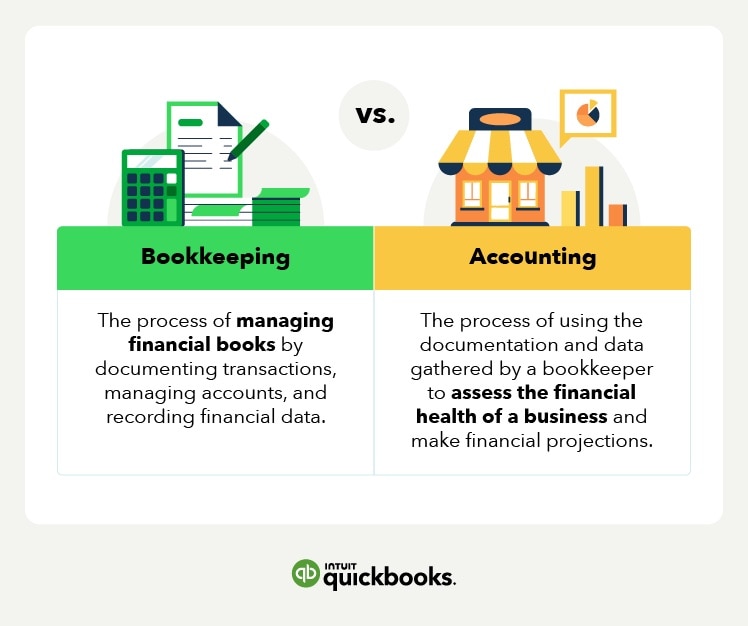
Bookkeeping focuses on managing financial books by documenting transactions, managing accounts, and recording financial data. This includes responsibilities like delivering balance sheets and income statements, confirming account accuracy by preparing trial balances, reviewing documents, and posting entries into accounting software.
Accounting focuses on using that data to assess the financial health of a business and make data-driven business decisions. This includes responsibilities like overseeing a bookkeeper's work to ensure accuracy, making adjustments to trial balances, generating financial statements, and producing financial reports that are needed to file business tax returns.
Below, we’ll take a closer look at bookkeeping vs. accounting, their key differences, and how working with bookkeepers and accountants can benefit your small business.