How to record unearned revenue
Businesses need to create an accounting entry for unearned revenue whenever a customer pays in advance for a good or service which hasn’t been delivered yet. You should also add it to your balance sheet.
Once the goods or service has been provided to the customer, the recorded “unearned revenue” must be changed to “revenue” within your business's accounting books.
Tip: Creating and adjusting a journal entry of unearned revenue will be easier if your business uses the accrual accounting method when recording transactions.
Unearned revenue journal entry
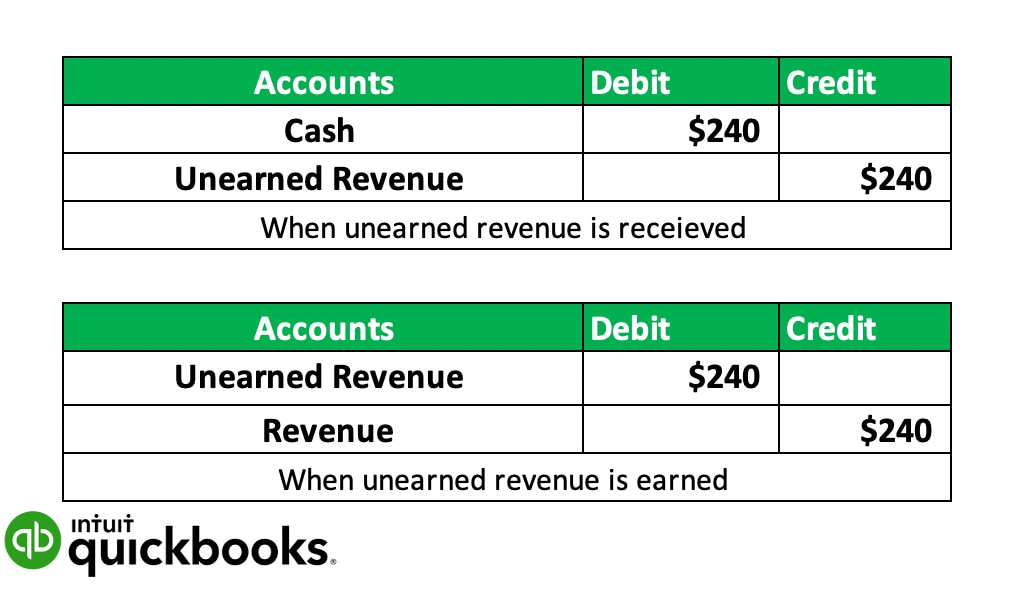
When a customer prepays for a service, you'll need to create an accounting entry for unearned revenue in your books. Using the double-entry accounting method, you'll credit unearned revenue and debit cash when payment is received. This journal entry of unearned revenue shows that your business has received cash but hasn't yet earned it.
Later, once you deliver the goods or services, you'll make a second entry to recategorise this liability as earned revenue. At this point, you'll debit the unearned revenue account and credit your revenue account.
To learn more about revenue recognition rules, check out our guide to AASB 15.