Debit vs credit accounting: Definition
Modern accounting uses a system called double-entry bookkeeping, where every financial transaction affects at least two accounts. "Accounts" are categories used to track and record different types of financial transactions—like sales, expenses, assets, and liabilities. Each account shows the running balance of a specific item, helping you understand where money is coming from and where it's going.
To track these changes correctly, you use two types of entries: debits and credits. Every time you record a transaction, you need both debit and credit entries that equal each other. This balance keeps your financial records accurate and helps catch mistakes.
Remember, debits and credits always work together. Every debit needs a matching credit of the same value, though they affect different accounts depending on the type of transaction.
What is a debit in accounting?
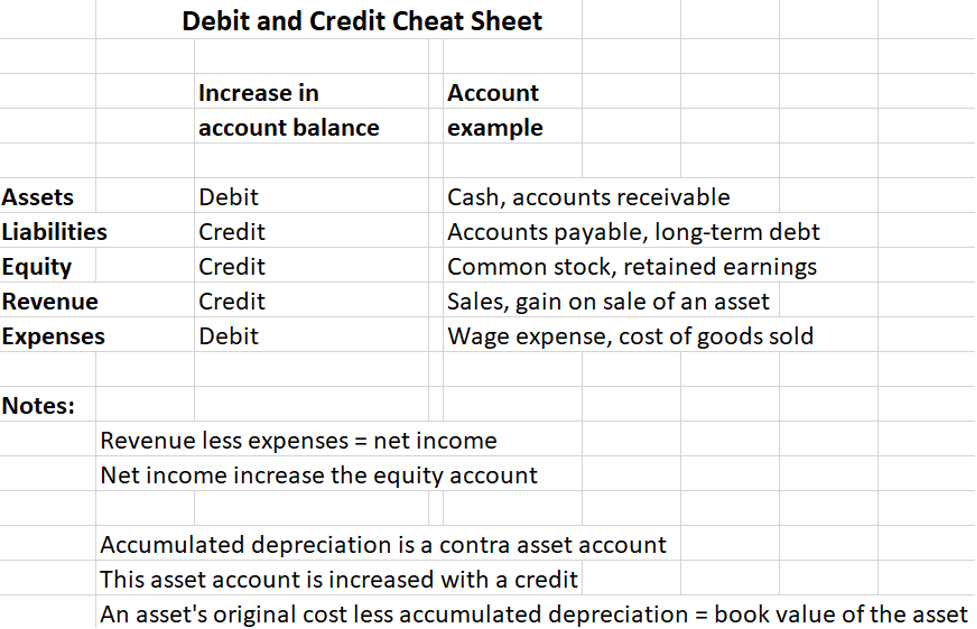
In simple terms, a debit is an entry on the left side of your accounting records. Debits typically increase asset and expense accounts, and decrease liability, equity and revenue accounts.
Accounts that increase with a debit include:
- Dividends: These are increased with a debit when a business pays dividends to its shareholders.
- Expenses: When you incur costs—like rent or utilities—you increase your expense accounts with a debit.
- Assets: Purchasing equipment, inventory, or supplies increases asset accounts through a debit entry.
- Losses: Any financial loss is recorded as a debit, increasing the loss account.
What is a credit in accounting?
Credits do the opposite to debits. They increase in liabilities, equity and income accounts—and decrease assets. If something brings money into your business, or represents money you owe, chances are you’re making a credit entry.
Here are some types of accounts that increase with a credit:
- Gains: Unexpected income that isn't part of your normal business.
- Income: Money received from activities outside your main business.
- Revenues: Money earned from your main business activities increases with credits, showing money flowing into your business.
- Liabilities: Money your business owes to others increases with credits, showing you've taken on more obligations.
- Stockholders' (Owner's) Equity: The owners' stake in the business increases with credits, showing additional investment or profits that are kept in the business.