5. Profit margin equation
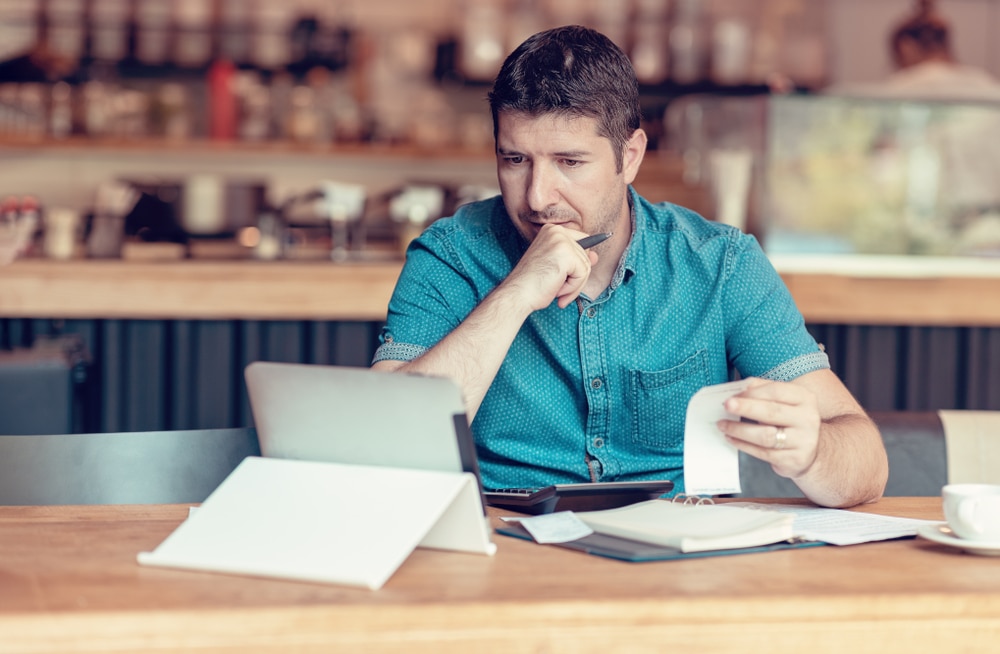
To get a better understanding of how your business uses its revenues to generate profits, use the profit margin equation. Not only this accounting formula shows the overall health of your company, but also helps derive a better strategy:
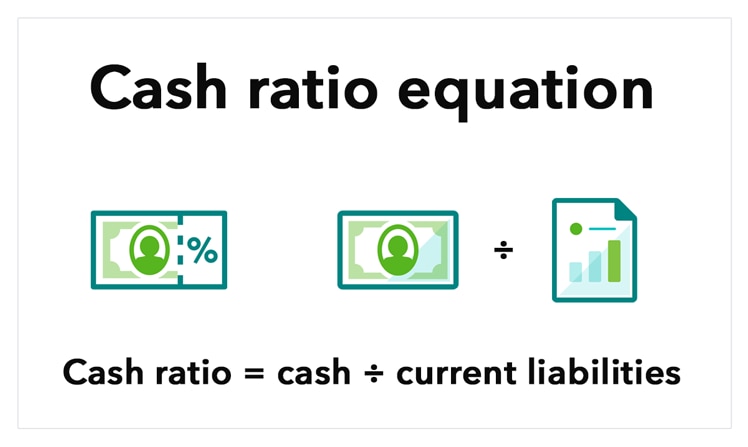
Profit margin = net income ÷ sales
What this accounting equation includes:
- Net income is the total amount of money your business has made after removing expenses.
- Sales refer to the operating revenue you generate from business activities.
When you divide your net income by your sales, you’ll get your business's profit margin. Your profit margin reports the net income earned on each dollar of sales. A high profit margin indicates a very healthy company, while a low profit margin could suggest that the business does not handle expenses well.
Remember, your net income is made up of your total revenue minus your expenses. If you have high sales revenue but still have a low profit margin, it might be a high time to take a look at the figures making up your net income.