Running your own small business can leave you overwhelmed with information, so you need useful metrics to make decisions. Many business owners use EBITDA and the EBITDA margin—calculations that take information from the income statement. Use this guide as a starting point to help you decide if you’ll use the EBITDA calculation. You’ll also want to understand the relationship between debt, taxes, cash flow, and a company’s profitability.

What is EBITDA? Definition, Formula, and How to Use It
What is EBITDA?
So, what does EBITDA stand for? EBITDA stands for “earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortisation”, and takes important information from a business’s income statement. The EBITDA calculation measures a company’s profits. But it’s important to note that EBITDA is different from net income (or net profit).
Depreciation expenses recognise the decline in value of capital expenditures, including vehicles, machinery, and equipment. Amortisation expenses record when intangible assets produce revenue. The bottom line is that every asset’s value reclassifies into non-cash expenses over time.
A company’s net income is total revenue minus expenses. EBITDA will add back four expense categories to the net income calculation. If a business generates a profit, net income will be less than the EBITDA balance because net income includes more expenses.
Calculating EBITDA can provide several reporting insights and help you make informed decisions about a company’s earnings. You can compare your financial performance to similar companies and assess the profitability of core operations.
Understanding the EBITDA formula
To understand EBITDA, review the multi-step income statement formula: revenue minus the cost of sales and operating expenses plus non-operating income.
The income statement and cash flow statement cover a period of time, but a balance sheet generates on a specific date. All three reports address financial health and a company’s operating performance.
To explain the EBITDA formula, take a look at Premier Manufacturing’s multi-step income statement.
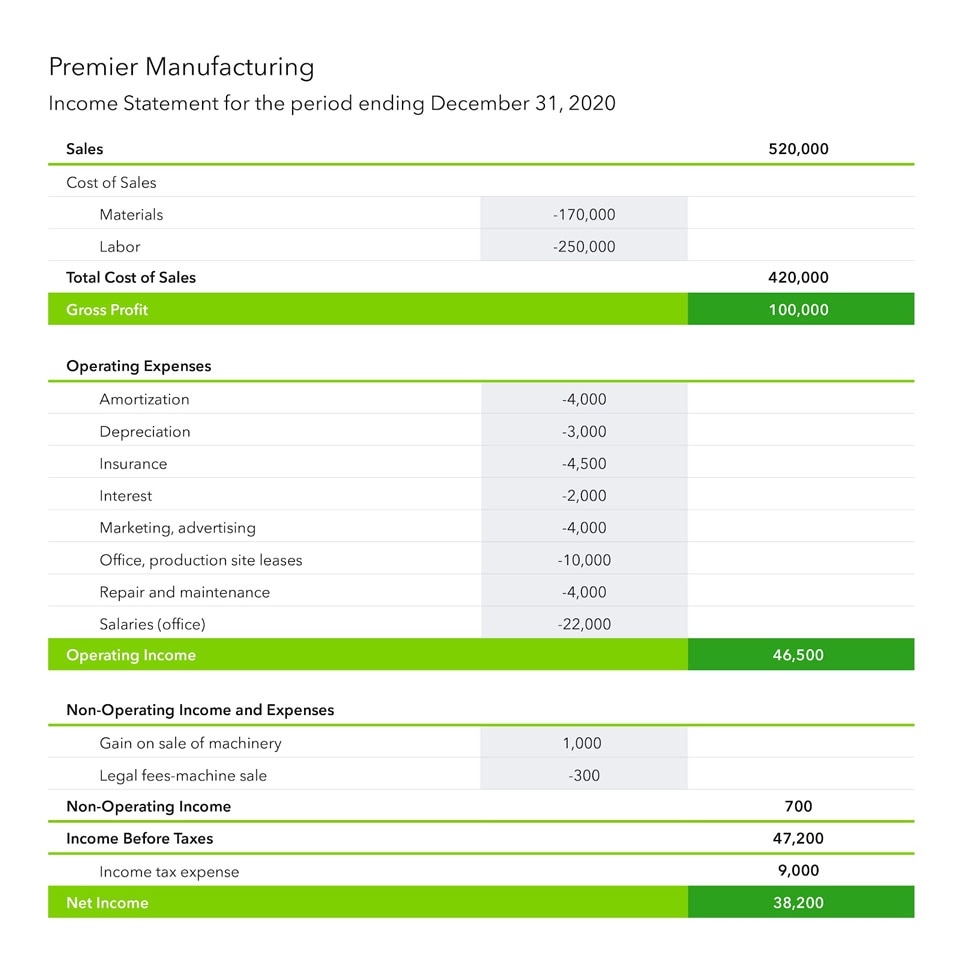
The formula includes the following components:
- The cost of goods sold includes material and labour costs directly related to the product or services sold. Sales minus the cost of sales equals gross profit.
- Operating expenses include a product’s indirect costs, including amortisation, depreciation, and interest expense.
- Gross profit minus operating expenses equals operating income. Premier has both non-operating income and expenses. The net amount ($700) is added to operating income to determine income before taxes.
- Income before taxes minus income tax expense equals net income.
Operating income is generated from day-to-day business operations, while non-operating income is unusual or infrequent. Premier is a manufacturer and not an equipment retailer. So the income and expense from the machine sale are posted to non-operating income.
Some business owners use EBIT, or earnings before interest and taxes, to assess a company’s ability to produce an operating profit. However, EBITDA is the more common metric to measure a company’s financial performance.
What is EBIT?
EBIT is a measure of operating profit, and it’s important to note that EBIT is different from a firm’s net income. A company’s profitability, when considering all expenses, is net income.
Net income (or net profit) is defined as revenue minus expenses, and EBIT excludes interest expenses and income taxes from the net income calculation. If a business generates a profit, net income will be less than the EBIT balance, because net income includes more expenses (interest expense and tax expense).
What is the Difference Between EBIT and EBITDA?
EBITDA is defined as earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortisation. On the other hand, EBIT does not add back depreciation expense and amortisation expense to the net income total.
Businesses use assets to produce revenue, and depreciation expense is posted as tangible (physical) assets are used up. Hillside, for example, owns a $10,000 machine with a useful life of 15 years, The machine’s cost is reclassified to depreciation expense as the machine is used to produce revenue.
In a similar way, amortisation expense is posted when an intangible asset is used in the business. Let’s assume that Hillside purchases a patent on a manufacturing process, and the patent has a remaining life of 20 years. Hillside will reclassify the cost of the patent to amortisation expense over 20 years.
Both EBIT and EBITDA add back interest expense and tax expense to net income. EBITDA also adds back depreciation expense and amortisation expense.
How to calculate the EBITDA formula
Multi-step income statements may vary slightly, but the EBITDA formula’s components should be easy to find. Interest, depreciation, and amortisation expenses are operating expenses. The tax expense calculation is at the end of the statement.
The EBITDA formula follows:
Net income + interest expense + tax expense + depreciation expense + amortisation expense = EBITDA

Using the formula, we find that Premier’s 2022 EBITDA balance is $56,200.
What is a good EBITDA margin?
The EBITDA margin is EBITDA divided by revenue. Most companies do not include a gain on sale as revenue if the gain is a non-operating income category. In Premier’s case, the gain on a machinery sale is not revenue. The only revenue category is $520,000 in sales.
Premier’s EBITDA margin is $56,200 divided by $520,000 revenue, or 10.8%. So Premier earns nearly 11¢ for every dollar of revenue.
To determine if an EBITDA balance is attractive, consider a company’s EBITDA over time and how the balance compares with industry benchmarks. If the balance increases from year to year, the business is increasing sales and controlling costs. The trend makes the company more valuable.
Potential buyers use EBITDA to compute the purchase price because the owner can distribute earnings as dividends. If two companies generate sales of $3 million a year, the company with the higher EBITDA is more valuable.
Why is EBITDA so important?
Those who use the EBITDA formula prefer to analyse a company’s performance based on day-to-day business operations. They disregard debt (interest costs), taxes, depreciation, and amortisation. Premier’s business operations include manufacturing, purchasing raw materials, paying employees, and billing customers. If you’re using EBITDA, you need to understand how debt and taxes can differ between companies.
EBITDA and debt management
A company’s capital structure has a big impact on the amount of debt a business carries and the interest expense. Every business needs capital to operate. Companies issue stock or borrow money to raise capital. Capital structure refers to the percentage of money a company raises by issuing stock or debt.
A startup without a history of predictable earnings may not be able to borrow money and may raise capital using stock. Banks are willing to loan money to established companies that can repay debt using a consistent flow of earnings.
Another factor is the number of assets needed for a particular company to operate. Some industries, such as banking, must raise a large amount of capital to hire employees, invest in technology, and operate physical locations. An online business may be able to operate with far less capital.
Pay close attention to the dollar amount of debt added back to earnings. High levels of debt generate more interest expense and require more cash for principal and interest payments.
EBITDA and taxes
Two companies in the same industry that generate similar profits can have very different tax expenses. The tax code is complex, and dozens of factors impact a company’s tax expense in a particular year.
For example, a tax carry-forward allows businesses to reduce current year earnings with losses incurred in past years. If a business uses a tax carry-forward, it lowers the tax expense in the current year. When the lower tax expense is added back to earnings, the current year's EBITDA is lower.
How EBITDA and cash flow differ
Generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) require companies to use the accrual basis of accounting to generate financial statements. Using the accrual method can generate large differences between EBITDA and cash flow.
The accrual method requires businesses to recognise revenue when they earn it and expenses when they incur revenue. Businesses don’t use cash inflows and outflows to determine revenue, expenses, or net income.
Assume that Premier purchases $1,000 in materials in January and pays $2,000 in labour costs in February to produce a piece of furniture. They finish the product and deliver it in early March for $4,200.
Accrual accounting requires Premier to post $4,200 in revenue and $3,000 in material and labour costs in March. Premier incurs other costs, including shipping, but the profit on the sale was $700.
This approach matches expenses and revenue in the same period and presents a more accurate picture of the profit.
What is GAAP?
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles, or GAAP, are a set of rules, standards, and principles that public companies must follow in some cases when making financial statements. GAAP rules guide you on how business transactions should be presented, disclosed, measured, and recognised on reports. GAAP also addresses revenue recognition, balance sheet, item classification, and outstanding share measurements.
Generally accepted accounting principles vary from country to country and currently there is not a universally accepted accounting recording and publishing system. For example, The GAAP was initially created in the United States and companies that have been publicly listed there need to follow, however, Canada also has its own GAAP.
EBITDA vs. cash flow
If you use the accrual basis to calculate net income, EBITDA will not reveal information about cash inflows and outflows.
The furniture sale example didn’t explain when Premier paid cash for the material and labour costs. Nor did it explain when the customer paid cash for the purchase. Premier earned a $700 profit, but the data provided didn’t explain the company’s cash inflows and outflows.
EBITDA is a useful tool to analyse profit but not cash flows. To understand a company’s cash position, review the statement of cash flows.
How QuickBooks can help with EBITDA
When you produce your financial statements each month and year, generate the EBITDA balance. Compare the balance to past periods, and determine if the trend is increasing or decreasing. Compare your performance to other businesses in your industry. Tools like QuickBooks Online Accounting Software can help you learn more about your business finances and perform more detailed analyses in less time.









