Payment terms
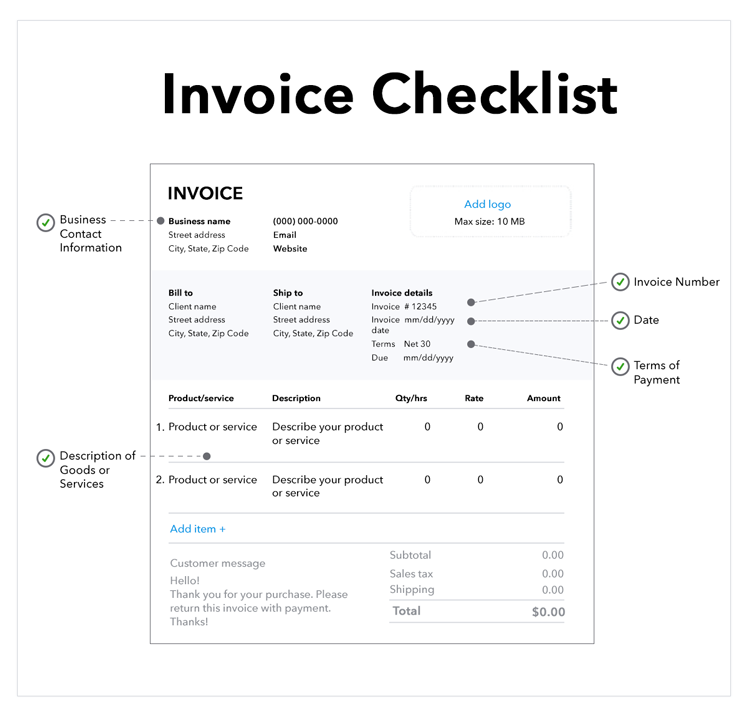
To increase the likelihood of receiving payment on time, you should provide clear details about payment expectations. Your payment terms should specify the amount of time the buyer has to pay for the agreed-upon purchase.
Choose invoicing terms that encourage early payment to maximise your cash position and your likelihood of getting paid. You may choose to collect half of the payment upfront, impartial payments over time, or as an immediate payment upon completion.
When setting payment terms, consider how to handle late payments. You should also consider a customer’s credit history when developing payment terms, particularly for large sales.
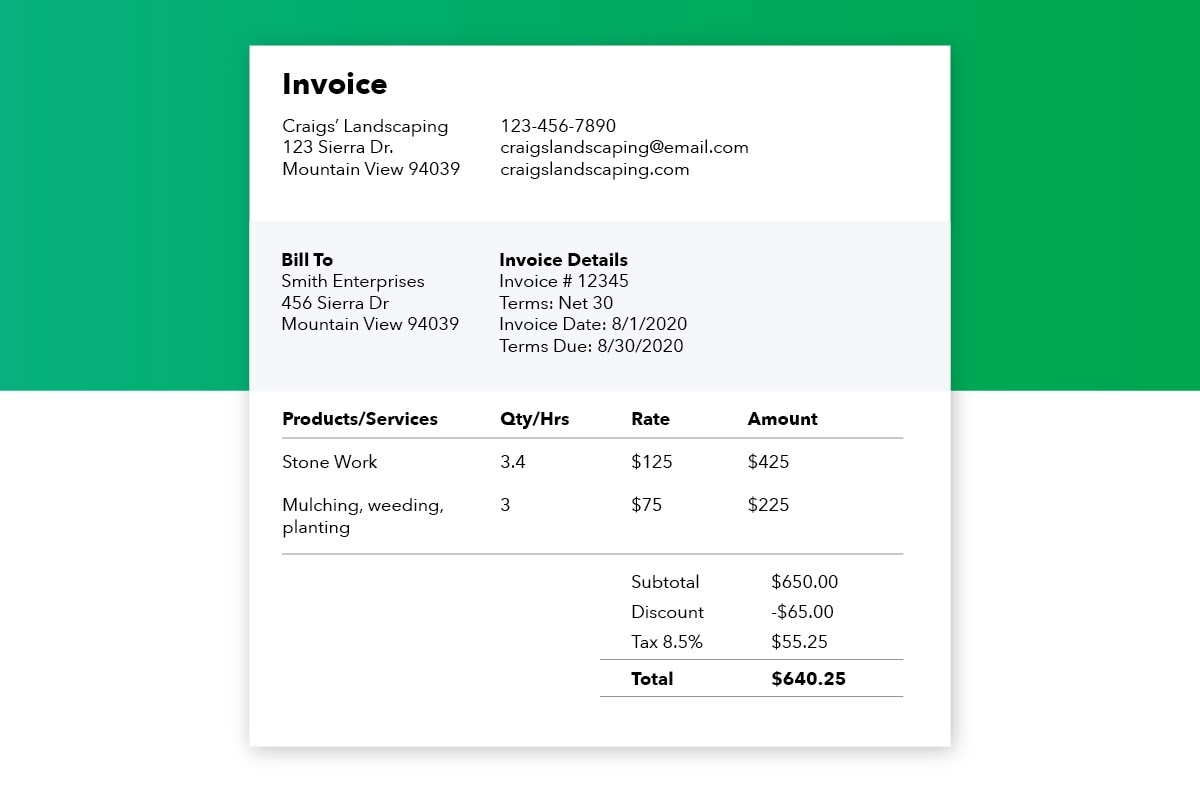
Once you’ve set your payment terms you can decide how long your customer needs to settle an invoice. Net 30 days (or “N/30″) is one of the most common terms of payment, which means that a buyer must settle their account within 30 days of the invoice date.
It’s important to remember that 30 days is not equivalent to one month. If your invoice is dated March 9, clients are responsible for submitting payment on or before April 8. Businesses may also set invoice terms to Net 60 or even Net 90, depending on their preferences and needs.
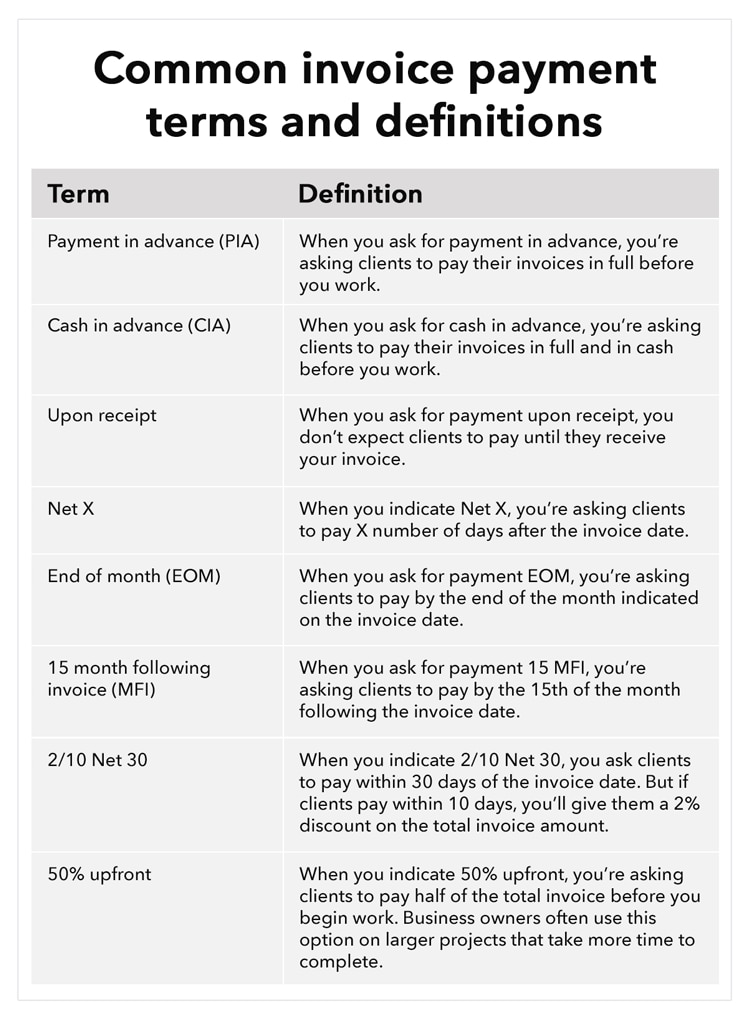
There are many different invoice payment terms, so it’s important to choose the right payment terms for your business. The chart below shows some of the common payment terms you may choose.