Most goods and services that are sold in Australia are subject to the Goods and Services Tax (GST). This tax was introduced on 1 July 2000 to replace multiple state and federal taxes with a single, broad-based consumption tax.
Here, we’ll explain the Goods and Services Tax and look at how it affects small businesses in Australia. We’ll also discuss the current GST rates in Australia and provide calculation guidance.
Keep reading to find out more, or jump ahead to a specific section:
- What is GST in Australia?
- What is the GST rate?
- How GST Works in Australia
- How to Calculate GST
- What’s the Difference Between GST & VAT?
- Why You Need To Register For GST
- Where To Register Online
- What Items are Exempt from GST?
- Do You Include GST in Tax Deductions?
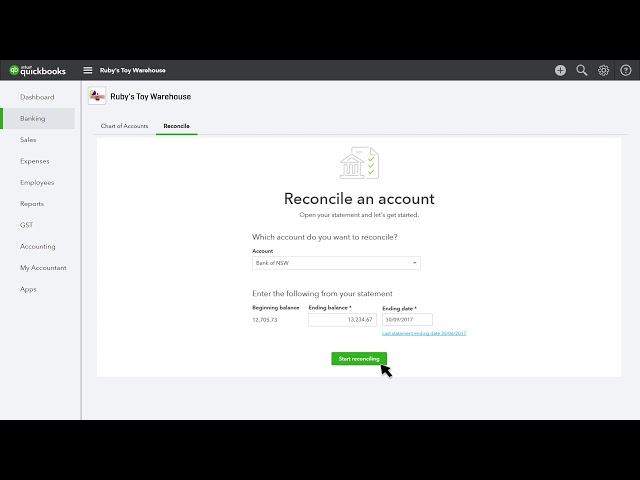
- How To Report GST
- Accounting For GST
- How to Manage GST with QuickBooks