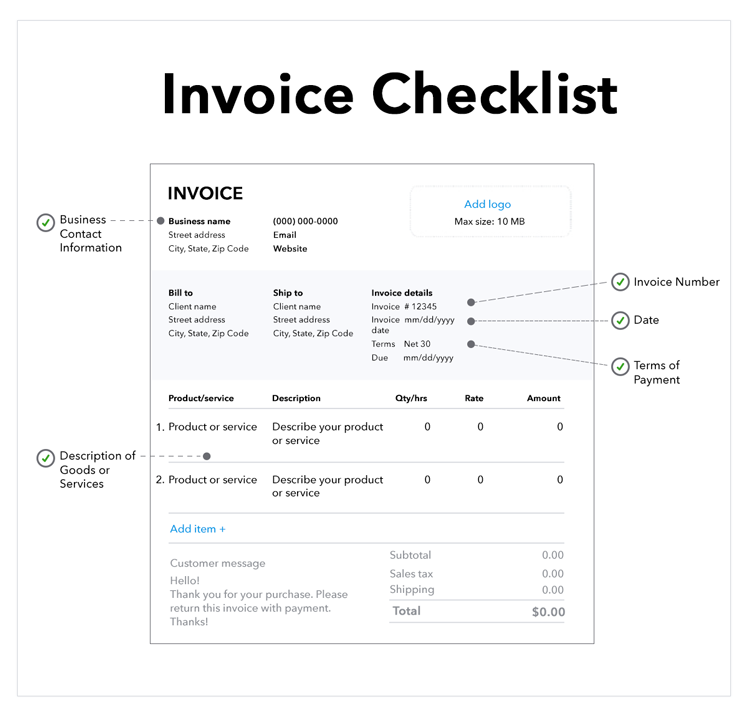
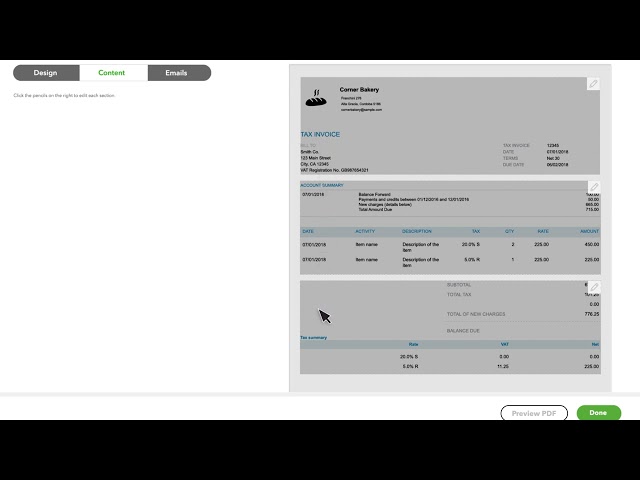
1. Invoice number
An invoice number should be assigned to each invoice you issue. This reference number establishes a paper trail of information for you and your customers’ accounting records.
Make sure you assign invoice numbers sequentially so that the number on each new invoice is higher than the last. Using electronic invoicing software can help make this process simple.
Invoices aren’t necessarily due immediately when customers receive them. You may choose to set invoice payment terms, like up to three months, in order to give your customers flexibility when managing their cash.
2. Invoice Date
The invoice date indicates the time and date when the supplier recorded the transaction and billed the client. The invoice date is a crucial piece of information, as it dictates the payment due date and credit duration. Generally, the due date is 30 days following the invoice date, but this can vary based on a company’s needs and the agreement with the client or buyer.
3. Business contact information
When you issue an invoice, you must provide your business contact information, including name, address, phone number, and email address, along with your client or buyer’s information.
4. Descriptions of goods or services rendered
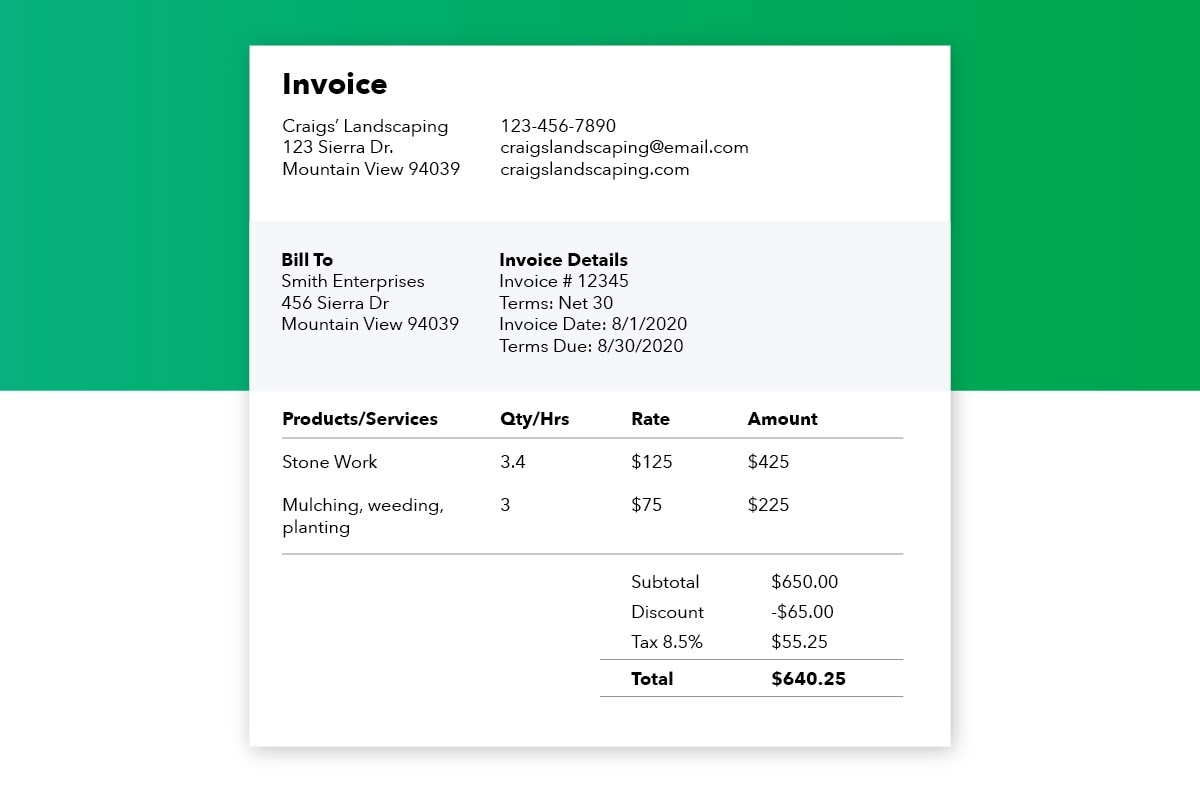
When issuing an invoice, you should enter every product or service you provide, along with the price and quantity for each, as a line item. At the bottom of the invoice, add up all of the line items, and apply any tax charges.
Here’s what to include when listing products or services provided:
- The date you completed service
- A description of services that specifies what you provided at the unit level
- How many units your customer ordered
- The rate per unit
- The total number of units
- The total amount due
- Any applicable tax
5. Payment terms
To increase the likelihood of receiving invoice payments on time, be sure to provide clear details about payment expectations. Your payment terms should specify the amount of time the buyer has to pay for the agreed-upon purchase.
Choose invoicing terms that encourage early or advance payment to maximise your cash position and the likelihood of getting paid. You may also choose to collect half of the payment upfront, collect partial payments over time, or require immediate payment upon completion.
When setting payment terms, consider how to handle late payments. You might also consider a customer’s credit history when developing payment terms, particularly for large sales. From there you can decide how long your customer needs to settle an invoice.
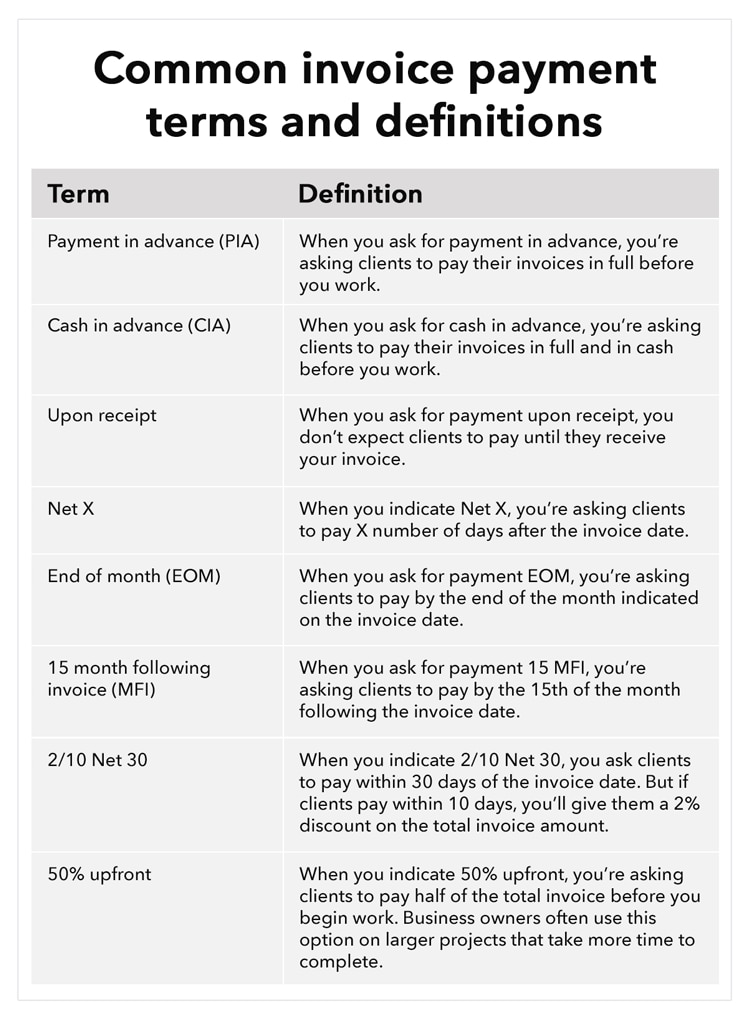
Net 30 days (or “N/30″) is one of the most common terms of payment, and means that a buyer must settle their account within 30 days of the invoice date. Businesses may also set invoice terms to Net 60 or even Net 90, depending on their preferences and needs.
It’s important to remember that 30 days is not equivalent to one month. If your invoice is dated March 9, clients are responsible for submitting payment on or before April 8.
There are many different invoice payment terms, so it’s important to choose the right payment terms for your business. The chart below shows some of the common payment terms you may choose.