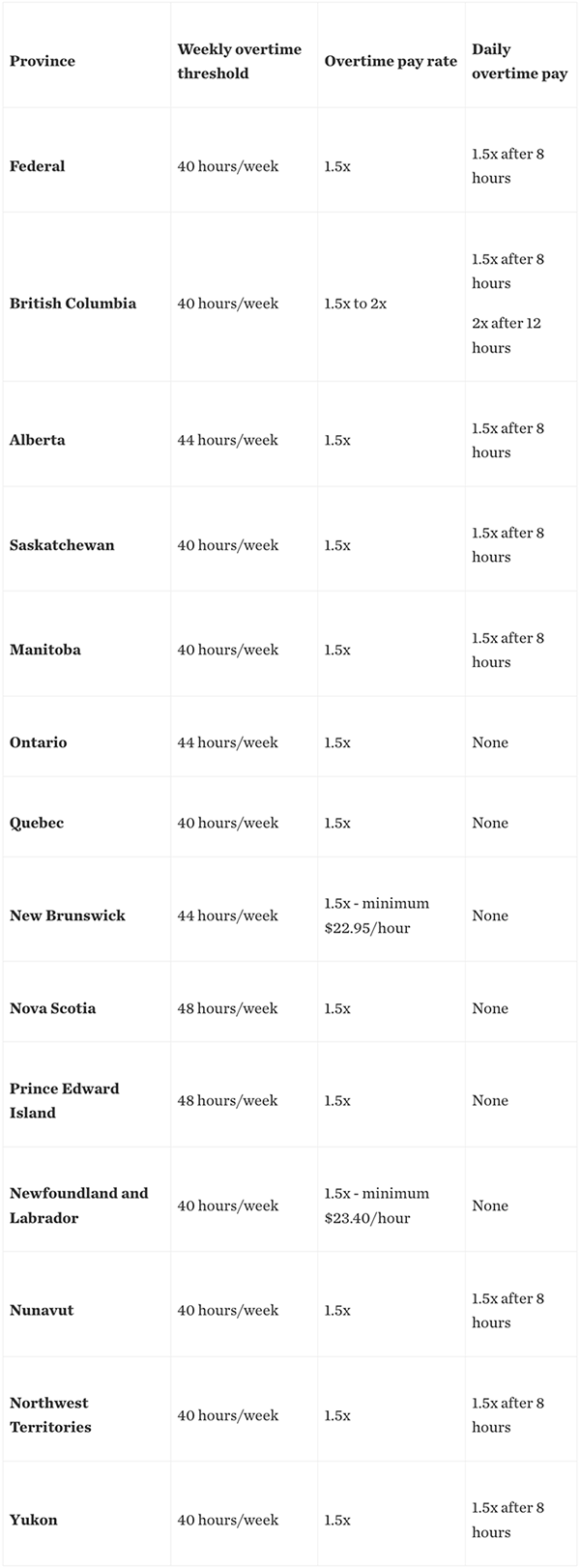
Overtime laws in British Columbia (B.C.)
The overtime laws in B.C. are governed by the province's Employment Standards Act (ESA). These regulations ensure employees are paid fairly for the extra hours they commit outside the standard work hours.
The following are the main points for overtime laws in B.C.:
- Overtime threshold: The province’s standard workday is 8 hours. Employees earn overtime pay for hours worked over 8 hours in a day or 40 hours in a week.
- Pay rate: Time-and-a-half is the compensation for hours worked between 8 to 12 hours in a day. Subsequently, employees are paid double their standard wage for every additional hour worked beyond the 12 hours.
- Exemptions: Workers in various professions — such as teachers, firefighters, and fishing/hunting guides — are exempt from overtime pay. However, if they work overtime, they should still be compensated for those hours at their regular pay rate.
Example calculation for overtime pay in British Columbia
If an employee works 45 hours in a week and earns $18 per hour:
Regular pay for 40 hours: 40 hours x $18/hour = $720
Time-and-a-half rate: $18/hour x 1.5 = $27/hour
Overtime hours: 45 hours - 40 hours = 5 hours
Overtime pay for 5 hours: 5 hours x $27/hour = $135
Total pay: $720 + $135 = $855
Example calculation for double-time pay
If a worker clocks in 14 hours of work in a day and earns $23 per hour:
Regular pay for 8 hours: 8 hours x $23/hour = $184
Time-and-a-half rate: $23/hour x 1.5 = $34.50/hour
Time-and-a-half hours: 12 hours - 8 hours = 4 hours
Time-and-a-half pay for 4 hours: 4 hours x $34.50/hour = $138
Double-time rate: 14 hours - 12 hours = 2 hours
Double-time hours: $23/hour x 2 = $46/hour
Double-time pay for 2 hours: 2 hours x $46/hour = $92
Total pay: $184 + $138 + $92 = $414
Specific overtime pay rules in British Columbia
The following are unique overtime pay rules in this province:
- Daily overtime pay: Employees earn time-and-a-half for hours worked beyond 8 hours in a day. They are also entitled to double-time pay once they have worked more than 12 hours in a day.
- Banking overtime: Workers can choose to bank their overtime hours instead of receiving immediate payment. This allows them to take paid time off at a later date. This must be established in a written agreement.
- Averaging agreement: Employees and employers can have a written agreement to average the variable hours over 1 to 4 weeks to determine overtime eligibility (if the weekly average exceeds 40 hours).