2. SAP
SAP is a global leader in enterprise application software. Large corporations widely utilize this company across various industries due to its comprehensive, robust, and highly integrated solutions. With over 50 years of experience in the industry, the company operates 109 development locations nationwide.
SAP’s features include modules for:
- Finance
- Supply chain management
- Sales
- Human Resources
- Customer relationship management
The company’s software provides real-time data access, advanced analytics, and forecasting tools. Due to its ability to offer deep customization and extensive functionality, SAP is well-suited for large enterprises and multinational corporations.
3. Oracle
Oracle is also a major player in the ERP industry with a strong focus on cloud-based solutions. The company’s Oracle Fusion Cloud ERP provides a modern, AI-powered platform that automates manual processes. Unlike SAP, Oracle Fusion Cloud ERP is built for both mid-sized and larger companies that want a cloud-first platform.
Oracle Fusion Cloud ERP includes built-in AI, machine learning, and analytics for real-time insights. The software offers modules for:
- Financial management
- Project management
- Procurement
- Risk management
- Enterprise performance management (EPM)
4. Microsoft Dynamics
Microsoft Dynamics is a suite of business applications that provides both ERP and CRM solutions. It easily integrates with other Microsoft products, like Microsoft 365 and the Power Platform. This ERP solution is ideal for small, medium, or large businesses that are already integrated into the Microsoft ecosystem.
Microsoft Dynamics uses AI and a low-code/no-code environment to simplify data management and automation. It offers modules for:
- Finance
- Supply chain management
- Commerce
- Human Resources
5. NetSuite
NetSuite is a leader in cloud-based business management software, offering a unified platform that integrates various business functions. This software is best for fast-growing organizations of any size that want to run their entire business from a single cloud platform.
Due to its native integration capabilities, which eliminate the need for third-party integrations, NetSuite can help with:
- Financial management
- Inventory
- Order management
- Supply chain management


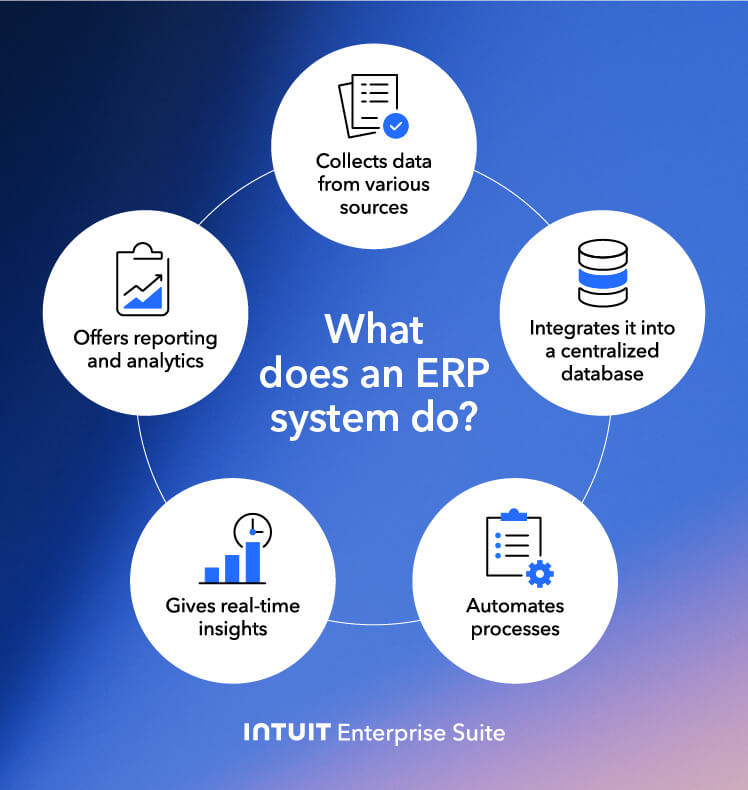
 ERP capabilities go beyond financial management. For example, businesses can use ERP for money services, marketing, and customer support.
ERP capabilities go beyond financial management. For example, businesses can use ERP for money services, marketing, and customer support.

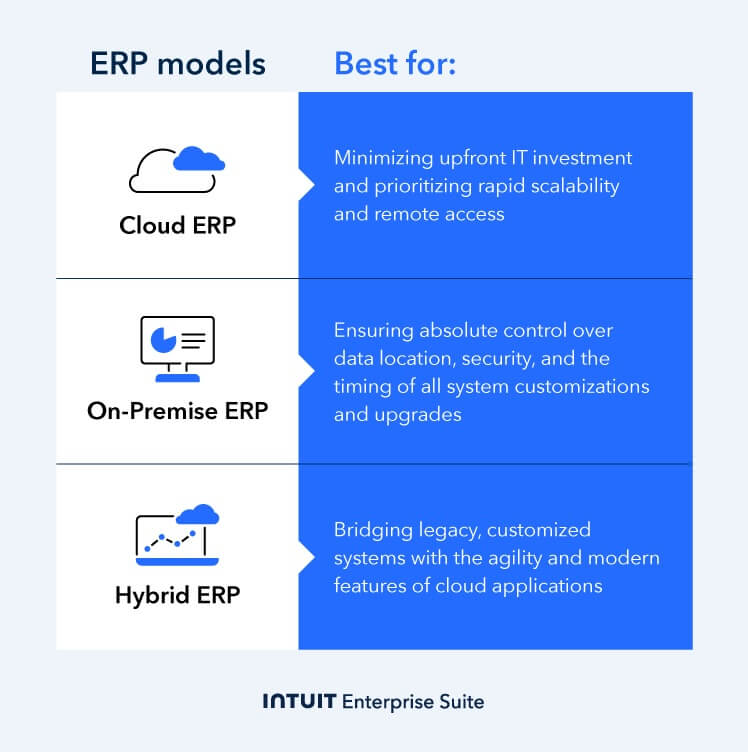

 Look for an
Look for an 




