Horizontal integration impact on market power and competition
When companies pursue horizontal integration, they often change the competitive dynamics of their industry.
Market concentration
Horizontal integration often leads to higher market concentration, where fewer companies control a greater market share. While this can boost the integrated company’s price control and bargaining power, it may limit consumer options and impact market diversity.
For instance, after Facebook acquired Instagram, it gained dominance in the social media space, potentially shaping market dynamics, user options, and advertiser costs.
Monopoly concerns
As companies gain control through integrations, there’s a risk of monopoly behavior, where excessive dominance reduces competition. This can stifle innovation, restrict market entry for new players, and drive up consumer prices. Major mergers in industries like technology and telecommunications frequently undergo regulatory scrutiny to ensure competitive fairness.
Regulatory and antitrust issues
Regulatory agencies actively monitor horizontal acquisitions to reduce anti-competitive practices. Antitrust laws protect consumer interests and keep markets open to competition.
When an acquisition or merger threatens to create a monopoly, regulators may impose restrictions or block the deal, as seen in the JetBlue and Spirit Airlines merger we mentioned earlier.
If the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and DOJ have reason to believe that a merger violates antitrust laws, the deal can be blocked. And existing mergers that have subsequently harmed competition can also be investigated.





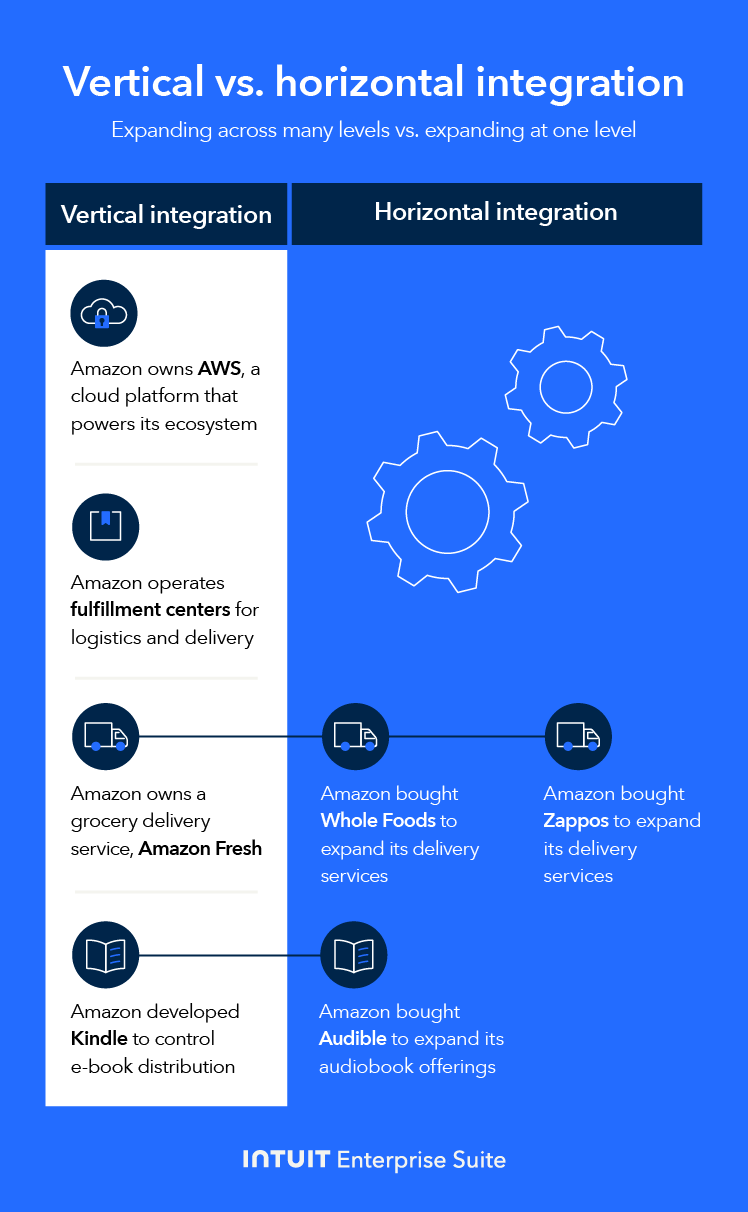
 Before pursuing horizontal integration, consider cultural fit, customer overlap, and regulator risks to ensure long-term value beyond immediate cost savings.
Before pursuing horizontal integration, consider cultural fit, customer overlap, and regulator risks to ensure long-term value beyond immediate cost savings.



