Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) implementation is more than just installing software—it’s a strategic move to streamline operations, reduce inefficiencies, and drive business growth. A well-integrated ERP system connects core functions like accounting, inventory management, and payroll, creating a seamless workflow that enhances productivity and reduces business costs.
For many companies, cost savings are a key motivator. A majority of Forrester survey respondents expect to cut technology expenses by implementing the Intuit Enterprise Suite ERP system: 82% anticipate savings on accounting-related costs, while 63% see reductions in email expenses by using Mailchimp through the platform.
When deciding to purchase an ERP system, it’s important to consider the benefits and drawbacks of an ERP.
In this guide, you’ll understand how to implement ERP systems, learn the mistakes to avoid, best practices, the usual timeline, and the approximate cost of implementation.
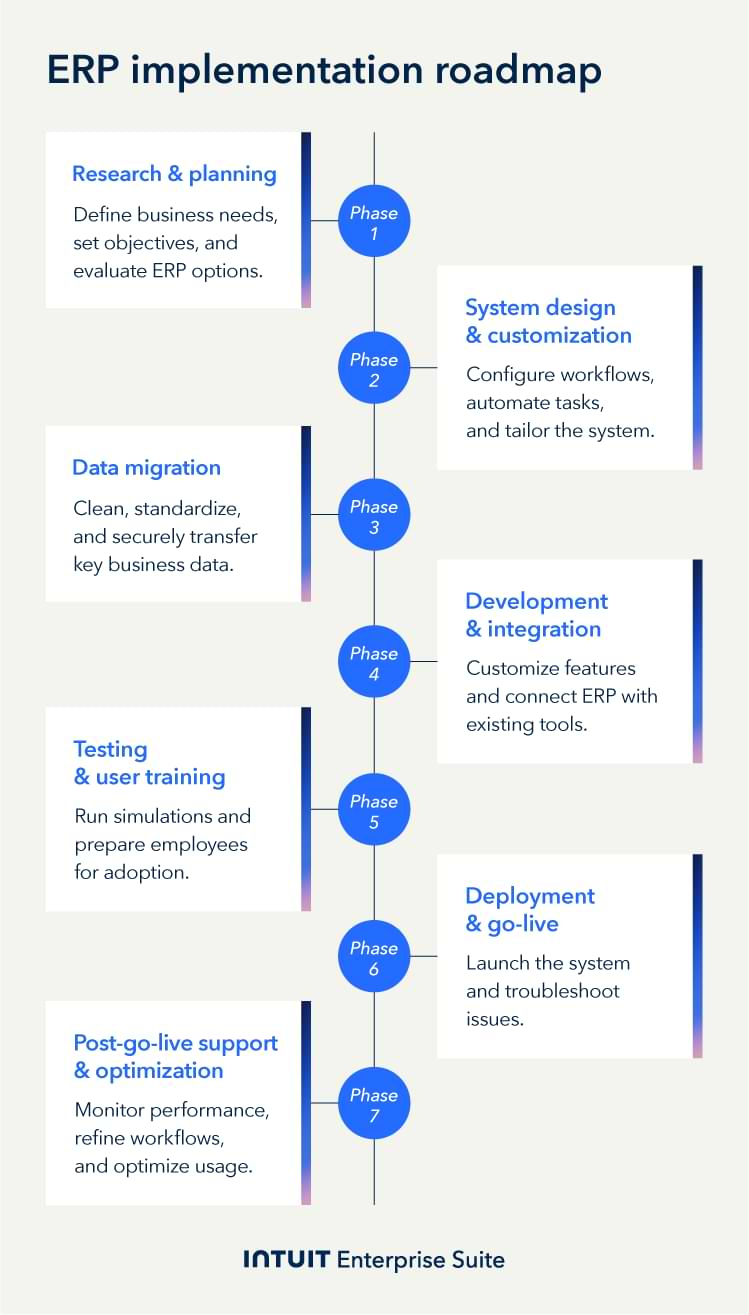
Let’s get started with the first step of the ERP implementation process: research and planning.
Key phases of an ERP implementation plan
Best practices for a smooth ERP implementation
How long does the ERP implementation process take?
ERP implementation costs and ROI considerations

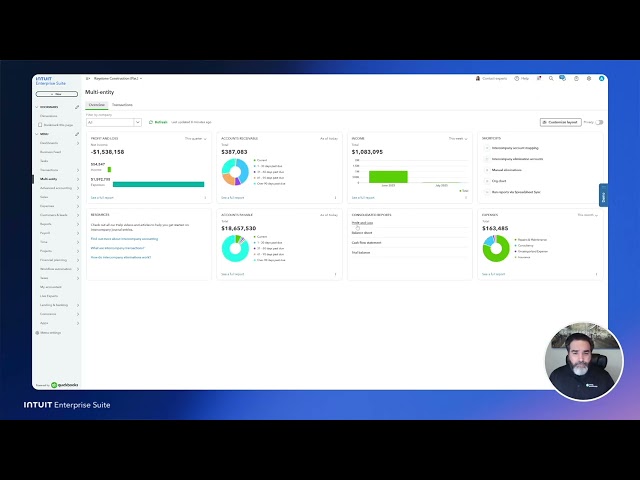
 Get feedback from key team members who will interact with the system daily. Their input during the configuration phase ensures the ERP is tailored to their needs, improving adoption and user experience.
Get feedback from key team members who will interact with the system daily. Their input during the configuration phase ensures the ERP is tailored to their needs, improving adoption and user experience.




