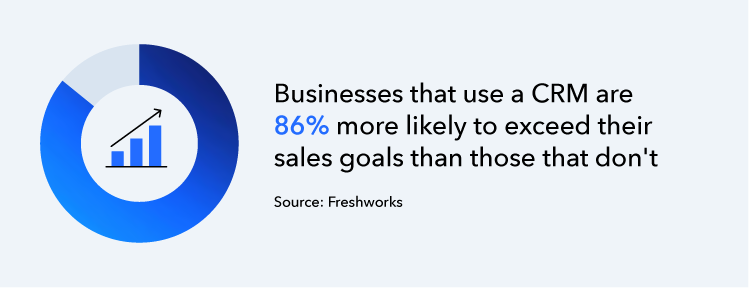
When it comes to streamlining business operations, two powerful tools often come up: Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems.
While both aim to improve business efficiency, they serve distinct purposes. Understanding the difference can help you decide which one fits your organization's needs—or if both are required.
At its heart, CRM helps businesses manage customer engagement, while ERP consolidates data from various business functions to ensure smooth operations. In this post, we’ll dive into the key features, differences, and benefits of each system, helping you make an informed decision on the best solution for your business.
Jump to: