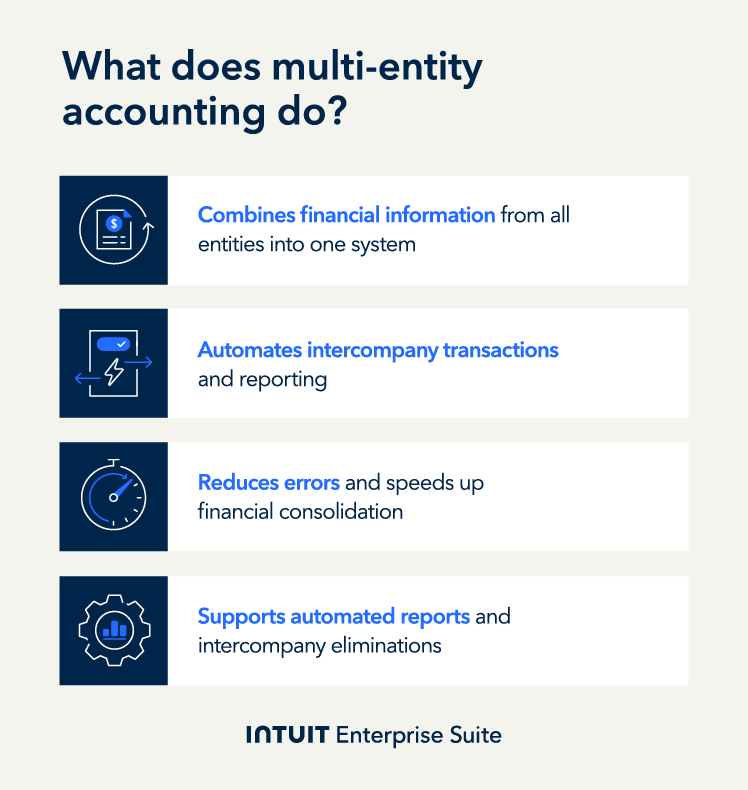
The building blocks of multi-entity accounting
At its core, multi-entity accounting aims to handle complex businesses, like enterprises. To truly understand its value, let's break down some key concepts.
What is an entity in accounting?
An 'entity' in accounting is any division or business unit that belongs to a larger organization and maintains its own financial records.
Think of a corporation with several subsidiaries, a retail chain with multiple branch offices, or even a nonprofit with different programs. Each of these is an entity, operating with its own financial statements, even if it's ultimately part of a larger parent organization.
What are multi-term entities?
This refers to an entity whose financial activities span multiple periods or terms, like fiscal years or specific project timelines. Since it introduces additional complexity, businesses should track financial data over these particular timeframes to ensure accurate financial reporting and compliance for each period.
What is multi-unit accounting?
Finally, multi-unit accounting involves managing the financial records for multiple units or branches within a single organization. This is different than multi-entity accounting, as all those units may be part of the same entity.
This approach enables a business to track each unit's income, expenses, and overall performance. At the same time, it allows your finance teams to consolidate all this data into a single, comprehensive financial report. You and other shareholders then get a more holistic view of the entire organization.
When paired with an integrated multi-entity accounting solution, like Intuit Enterprise Suite, multi-entity accounting provides the clarity and control you need to grow your business.