How to perform ERP data analysis
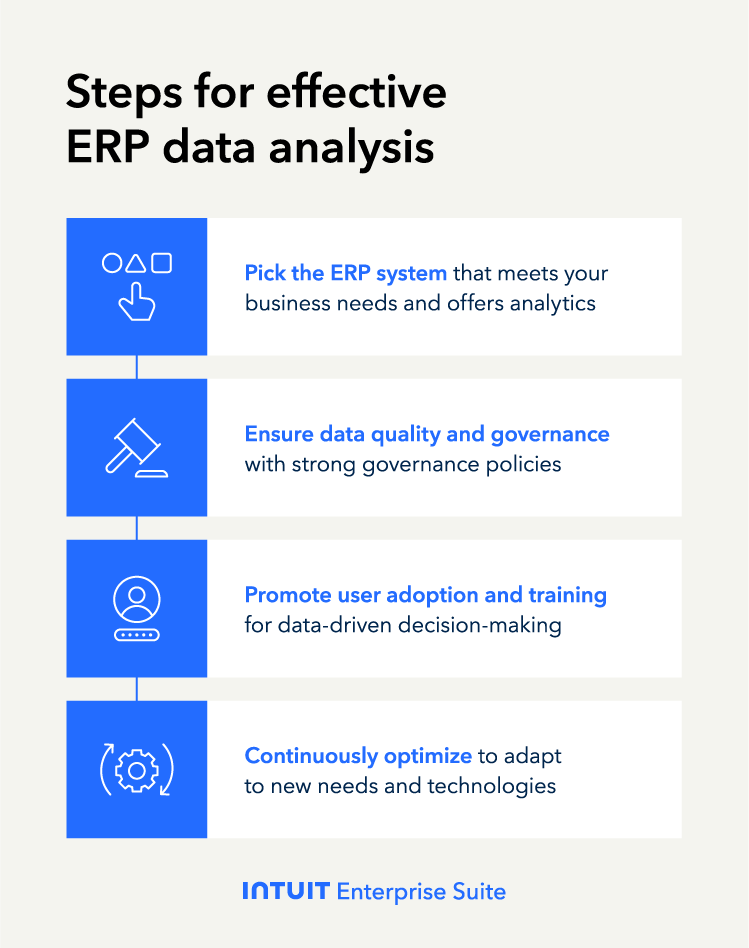
Effective ERP data analysis requires a strategic approach. From selecting the right ERP system to ensuring data quality and fostering user adoption, each step plays a critical role in maximizing the benefits of ERP analytics.
Choosing the right ERP system
Look for a system that aligns with your business needs and offers robust ERP analytics capabilities. Consider scalability, ease of integration with existing tools, and the ability to customize reports and dashboards to suit your specific requirements.
Data quality and governance
High-quality data is the foundation of accurate ERP analysis. Establish clear data governance policies to ensure data is accurate, complete, and up-to-date. Also, implement processes for regular data cleaning and validation to prevent errors and maintain data integrity—essential for reliable analysis and reporting.
User adoption and training
Successful ERP implementation relies on user adoption and proper training. Ensure employees understand how to effectively use the necessary accounting software, like an ERP system, and know the benefits of data-driven decision-making. Don’t forget to provide ongoing training and support to help users leverage the system's full potential and integrate it into their daily workflows.
Continuous improvement and optimization
ERP data analysis is not a one-time setup but an ongoing process. Regularly review and refine your data analysis practices to adapt to changing business needs and emerging technologies. Don’t overlook the importance of regularly evaluating system performance and seeking user feedback. Make adjustments based on your analysis to improve the effectiveness of your ERP analytics and overall data strategy.

 Enhance your ERP analytics by incorporating external data, such as market trends or customer feedback, for a more comprehensive view.
Enhance your ERP analytics by incorporating external data, such as market trends or customer feedback, for a more comprehensive view.


 Benchmark your performance. Regularly compare your analytics results with industry benchmarks to gauge performance and set realistic improvement goals.
Benchmark your performance. Regularly compare your analytics results with industry benchmarks to gauge performance and set realistic improvement goals.