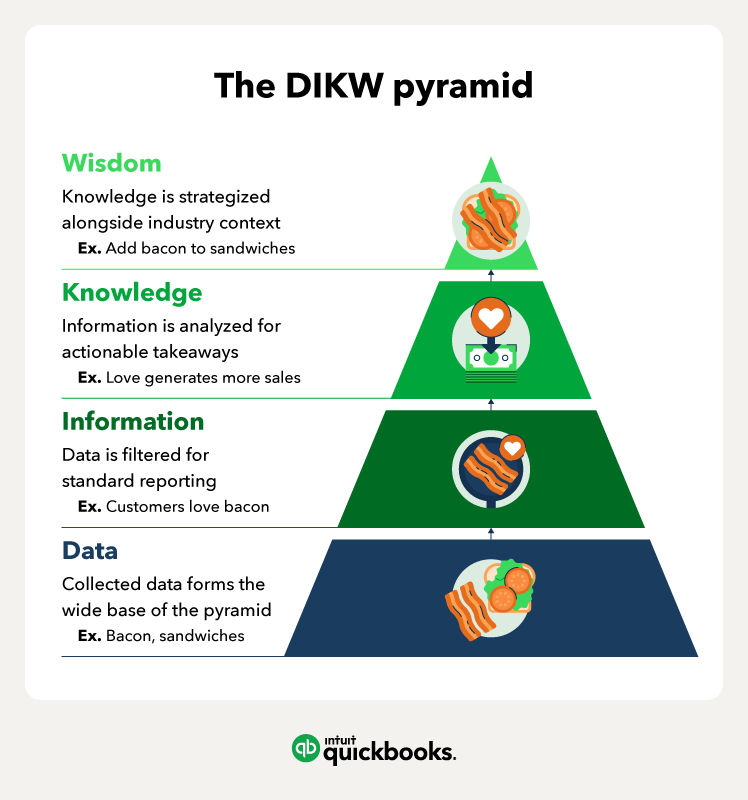
Using big data: Data structure and organization
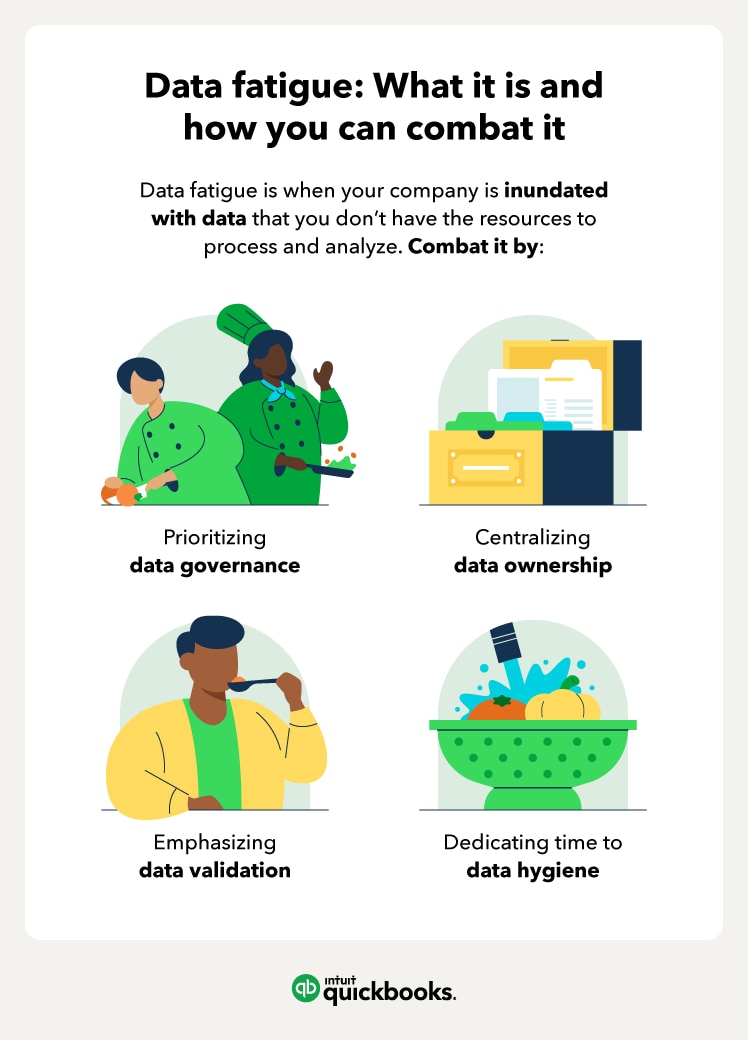
Big data comes from a variety of sources at a high velocity, just like the GPS example above. With so many sources (also known as the “data lake” of available data) and so little control over standardization, collected data can wind up in all sorts of packaging arrangements. This can get messy fast if there’s no remedy to tidy up the data as you collect it.
Fortunately, data governance efforts can help you rein in the mess. Data governance is a set of organizational rules for managing data in order to standardize its value, velocity, and veracity. Data governance policies can also ensure you always know:
- Who owns what when it comes to your data.
- When to audit data for industry compliance.
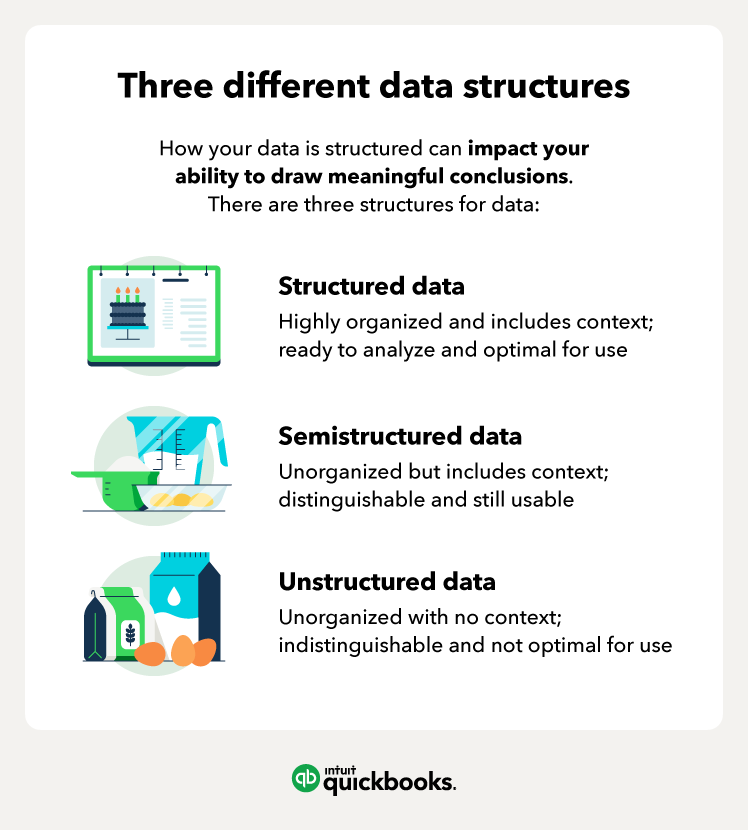
There are three overarching structures for collected data:
- Structured data is organized and readily available for analysis.
- Semistructured data is not organized but contains metadata to distinguish it.
- Unstructured data is not organized and not optimized for usage.
Example: Think of it this way. Structured data are complete reports and records organized with advanced accounting software, semistructured data are complete records with context that need to be organized and translated into reports, and unstructured data are piles and piles of notes and receipts.
No one wants to dig through a pile of receipts and the same is true for businesses working with unstructured data. It’s too complicated to untangle and isn’t optimal for most small businesses. That’s why you should think about how you collect your data—the more organized it is when you receive it, the less work you need to do.
Structured and semistructured big data can have a heavy influence on financial reporting, including shaping your company’s risk management, marketing efforts, and even customer relations.
Proactive risk management
There are numerous metrics that can help you to gauge the health of your business and forecast financial risks. Using big data, you can monitor your company’s overall progress and report on specific metrics like:
- Vendor risk management (VRM)
- Fraud detection and prevention
- Customer loyalty and churn
- Market share capture
Using risk management software for specific data collection can help you organize these insights into takeaways for financial reports on how to mitigate risks and reduce losses.
Targeted marketing
Marketing is a multifaceted industry that requires a multichannel or omnichannel approach for true success in today’s business landscape. With comprehensive views of your target audiences and detailed analysis of customer engagement, big data helps to:
- Improve brand awareness
- Increase customer acquisition
- Save long-term marketing costs
Big data analytics for a tailored marketing approach involves looking at inputs like web usage and financial transaction history to spot prospective customers and find new ways to convert them. Those conversions are optimal for financial reporting and marketing plans, as are the details behind the conversion and how you collected them.
Comprehensive CRM
Detailed analysis of customer behavior patterns allows you to put your finger on the pulse of your client base: What do they need from you that you aren’t providing, and how can you pivot to address that need? When you infuse customer relationship management with big data analytics, you can more effectively:
By harnessing big data, you can create a more positive customer experience that translates into higher customer loyalty and lifetime value. Tracking long-term customers over time leads to valuable insights on your products and services that are useful context to include in financial reports.