As a business scales to serve customers, grow revenue, and increase profits, it often requires new tools and technology. Growing companies need different types of enterprise resource planning software (ERP) solutions to help connect disparate business applications, automate back-office workflows, and bring greater visibility to operations across the organization.
Selecting the right ERP for your business will help you streamline business operations across departments and geographies, improve decision-making, and create greater value for your business and your customers.
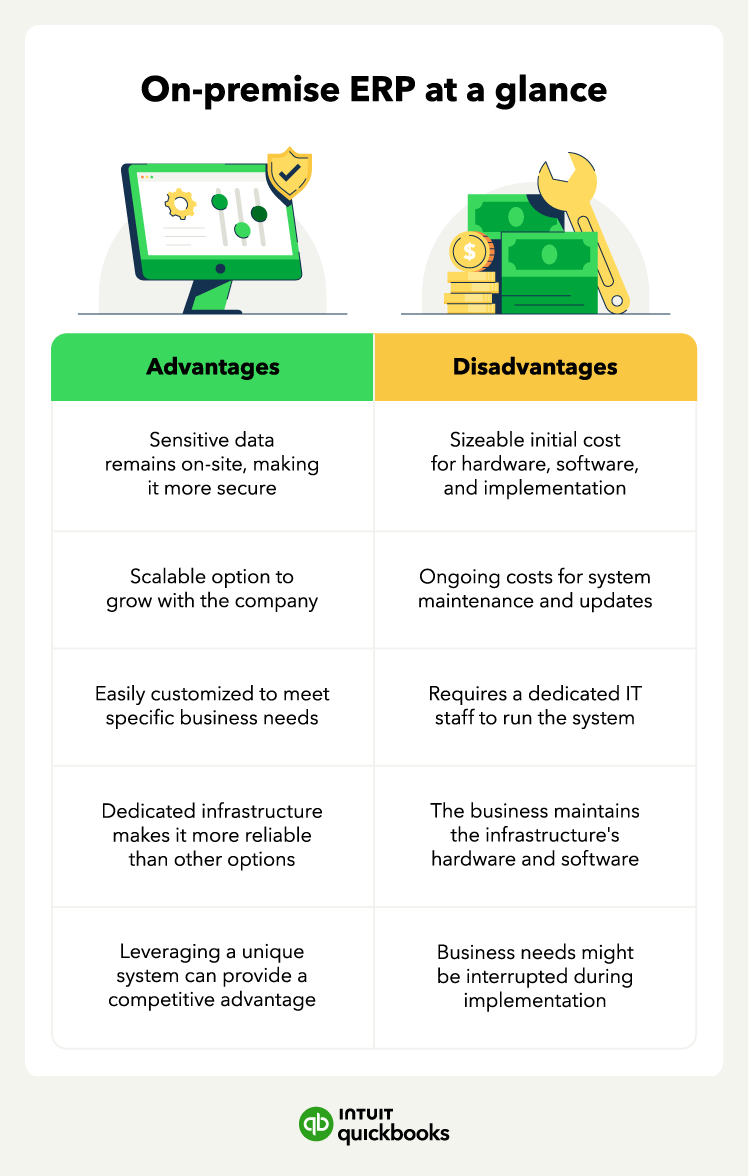
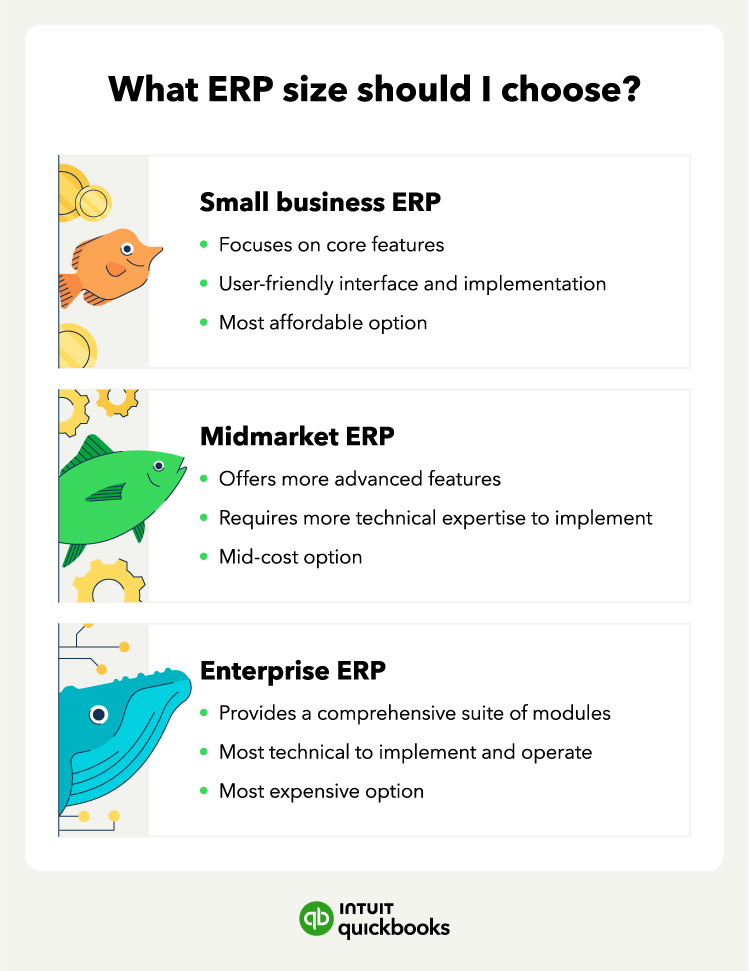
You can choose three types of ERP software options by deployment type: on-premise, cloud-based, or hybrid. Plus, there are ERP solutions for small and mid-market businesses, as well as enterprise-level corporations, making this a versatile option for all.
Jump to:


 Do a careful cost-benefit analysis of what your small business needs versus the features any ERP you're considering provides. Your business may be able to run on simpler accounting and financial management software like
Do a careful cost-benefit analysis of what your small business needs versus the features any ERP you're considering provides. Your business may be able to run on simpler accounting and financial management software like 


