Running your own business presents unique opportunities for you to be your own boss, bring your entrepreneurial vision to life, and direct your financial future. But to avoid being among the 18% of small businesses that fail within their first year, you’ll want to take every precaution behind the scenes.
Creating a business budget is an excellent first step for any new business owner. By taking a closer look at your assets, expenses, and financial goals, you can craft a better plan for the future of your booming business. And ideally, you can reap some of the monetary benefits.
Let’s take a closer look at how to create a business budget and discuss the benefits of budgeting. You will even find some helpful resources and a business budget template we hope you can leverage moving forward. With the right tools and processes, you can use business budgeting to your advantage.
• What spreadsheets to keep for your small business
• Benefits of a budget for your business
• What’s included in a business budget?
• How to create a budget for a business
• Small business budget customization
• Budgeting best practices for business
• Free business budget templates
What is a business budget?
A business budget is an outline of an organization’s revenue, expenses, and profit over a period of time—generally monthly, quarterly, or annually. A good business budget assigns a purpose to every dollar your business earns. For instance, some money might go toward bills or business growth. Others will help fund daily operational expenses and take-home pay for yourself and your staff.

Solid business budget planning will provide a road map for spending and earning. It’ll create a lens into your organization’s financial future and facilitate better decisions all around. Ready to get your business idea off the ground? You’ll need to consider startup costs. Wondering if you can or should purchase new equipment this year? Refer to your business budget plan.
Maybe you’re looking for ways to cut down on expenses. Your business budget can present a view of your financial health, including where you’re spending money and where you might benefit from cutting back. With better foresight, you can cultivate stronger business performance and improve earnings from the last quarter or the last year.
Types of budgets for businesses
Here's a breakdown of the most common budgeting methods for businesses:
Master budget
This is the big-picture budget, encompassing all aspects of your business's finances. It includes projected income, expenses, and cash flow for a specific period, usually a year. It’s like your financial roadmap, which can influence and guide your overall financial strategy and decision-making.
Operating budget
This budget focuses on your day-to-day operations. An operating budget includes anticipated revenue and expenses related to your core activities, such as sales, production, and marketing. An operating budget helps you track performance, identify potential cost-saving opportunities, and ensure your daily operations are financially sustainable.
Cash flow budget
A cash-flow budget provides a detailed projection of your cash inflows and outflows over a specific period. It helps you anticipate periods of high or low cash flow, allowing you to proactively manage your finances and avoid potential shortfalls. This can be especially important for businesses with seasonal fluctuations.
Sales budget
Focused specifically on projected sales revenue, the sales budget is often broken down by product, service, or customer segment. It's a component of the overall master budget and drives many other financial projections.
Production budget
For businesses that manufacture products, this budget outlines the anticipated costs and quantities of production, including raw materials, labor, and overhead. It ensures that production aligns with projected sales and helps with inventory management.
Labor budget
This budget focuses on labor costs, including wages, salaries, benefits, and payroll taxes. It helps businesses plan for staffing needs, optimize workforce allocation, and control labor expenses.
Capital budget
A capital budget deals with long-term investments in assets like equipment, property, or technology. It helps businesses evaluate the financial viability of major projects and plan for future growth.
Financial budget
Encompassing the overall financial picture of the business, a financial budget includes projected financial statements like the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement. It helps businesses assess their overall financial health and make strategic decisions.
Static budget
A static budget remains fixed, regardless of changes in sales or production volume. It's useful for planning and evaluating performance against a set target, but it may not be as flexible as other budget types.
Budgeting methods
Budgeting helps you track where your money is going and plan for future expenses. But there are different budgeting methods you can use, based on your organization’s demands and preferences. Let’s explore a few of the most common budgeting methods.
Incremental budgeting
The incremental budgeting method starts with your previous budget and adjusts it based on anticipated changes. It's a simple and easy-to-implement method, but it might not be the most accurate or flexible approach, especially for businesses with fluctuating income or expenses.
Zero-based budgeting
This detailed budgeting method starts from scratch and requires justification of every expense and fund allocation based on priority. It is not based on previous budgets or historical data. Because it is so thorough, it can be time-consuming and might not be suitable for all businesses. However, it’s a valuable method for scrutinizing expenses and where costs could be cut.
Value proposition budgeting
This budgeting option, which is also called priority-based budgeting, focuses on aligning your budget with your organization’s core values, strategic goals, and what’s most important to the customer. It’s based on allocating spending toward the activities that directly contribute to your value proposition and long-term success.
Activity-based budgeting:
Businesses with diverse operations or that rely on project-based income often use activity-based budgeting. This method links your budget to specific activities or projects, allowing you to track costs and allocate resources more effectively.
The effectiveness of a budgeting method often varies based on a business's specific industry, context, and size. Some companies may choose to combine elements from multiple budgeting strategies, creating a hybrid approach.
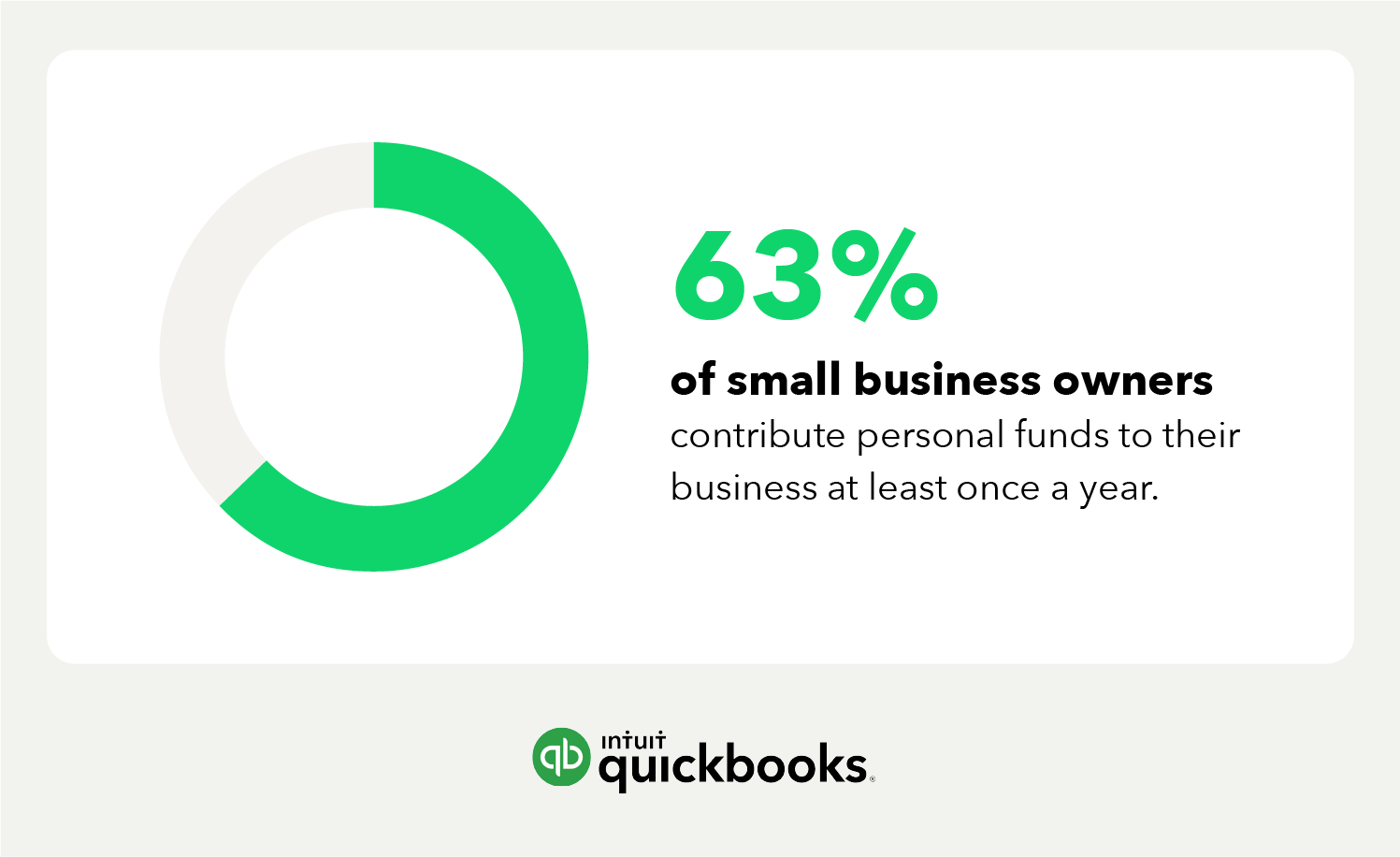
Benefits of a budget for your business
“A business budget is a financial road map to success, a vision of where you want to take your business for the upcoming 12 months,” the FDIC says. What’s more, research has suggested that business budgets offer the following benefits:
- Give business owners more freedom to run their organizations with confidence.
- Allow business owners to identify cash flow and spending problems.
- Empower business owners to have a greater sense of control and insight when dealing with financial challenges.
- Help business owners and decision-makers predict cash flow and identify trends.
- Demonstrate positive money management to lenders and investors.
- Give you the chance to identify and rectify problem areas quickly.
Bottom line: Consider a detailed budget one of your key business needs.
What’s included in a business budget?
A business budget takes into account an organization’s total revenue and expenses to reveal net profit (or loss). The FDIC says the best business budgets comprise the “nuts and bolts” of everyday revenue and expenses like:
- Average order amount
- Number of product orders per month
- Billable hours
- Average payroll costs
- Material expenses
- Rent, mortgage, and utilities
When building a business budget, business owners should bear in mind that output depends on input. Make sure you’re collecting accurate data points whenever you’re dealing with your business’s finances. A simple mathematical error or typo can lead to confusion or, worse, uninformed financial decisions.
How to create a budget for a business
Now you know what a business budget is, why it’s important, and the essential components. Let’s now take a look at the steps you need to take to create one.
1. Calculate all forms of income
Whether you’re optimizing your personal spending or building a business budget, your first step should be aggregating all of your forms of income. Your net income determines how much you can afford to spend. It also indicates your take-home pay and whether your business performance is growing or stagnating.
To find out how much money your business is bringing in, refer to your profit and loss statements. Depending on your business model, you may have several income sources, so be sure to include any and all revenue streams in this section.
2. Subtract your fixed expenses
Once you’ve added all of your business’s income together, you can subtract your fixed costs. Fixed costs are expenses that remain consistent throughout the year. Whether you pay bills monthly, weekly, or annually, you can expect to spend a set amount of dollars on each expense. These costs are easy to predict, so they’re easy to work into your budget. The one-off expenses, or variable costs? Not so much—more on that in a minute.
Examples of fixed expenses include:
- Commercial rent or mortgage
- Operational utilities
- Loan payments
- Insurance bills
- Employee salaries
Once you’ve tallied up your fixed expenses, you can subtract that number from the total income you calculated in step 1.
3. Subtract your variable expenses
In addition to your fixed costs, you might anticipate monthly operating expenses that may not always be the same amount. These variable expenses may be harder to predict, but you can refer to old receipts and invoices to estimate them.
Examples of variable expenses include:
- Material costs
- Commissions
- Billable staff wages (freelancers, outsourced work, etc.)
After identifying your variable expenses and estimating how much they cost each month, subtract the amount from your income.
4. Prepare for emergency and one-time expenses
Life is full of unexpected circumstances. As a business owner, you’re likely familiar with unexpected expenses. New equipment, hiring expenses, and unplanned events can add up, so it’s wise to plan ahead as much as you can.
You can’t predict when you’ll need to pay for an emergency expense or how much it might cost, but you can set aside a cash reserve to lessen the burden.
5. Create a profit and loss statement
You’ve accounted for your income and fixed, variable, and emergency expenses. Now you can better understand your business finances by creating a profit and loss (P&L) statement. A P&L statement is a high-level overview that shows whether your organization is profitable or in the red.
When you add up all of your income then subtract your total expenses, you should have a positive or negative number. A positive number indicates that you’re in the black and, therefore, making money. A negative number indicates that you’re in the red and, therefore, burning a hole in your pocket.
Your P&L statement serves as a baseline for creating your business budget. You can access your profit and loss statement, track trends, monitor invoices, and more from your QuickBooks account.
Keep in mind that your profit and loss statement may not always show you the results you want. But with better business budgeting and forward thinking, you can set yourself up for a brighter and more profitable future.
6. Draft your business budget
After reviewing your P&L statement, you’ll have a better idea of where you’re spending your money—and if you’re spending responsibly. With this data in mind, you’re ready to draft your business budget for the next year, quarter, or month. Most businesses opt for quarterly budgets.
A basic budget outlines your expenditures and designates limits for each over a given period. This outline can help you determine whether you’re earning and spending within your abilities. With QuickBooks, you can easily glean insight into spending patterns and assess where your business stands financially.
Small business budget customization
Every small business has a niche, workflow, and financial goals. So it’s important to remember that there’s no one-size-fits-all approach to business budgeting. As you learn how to build a business budget and experiment with the strategies you’ve learned, consider the following:
- Seasonality may affect customer buying behaviors, depending on your business type. Consider these fluctuations in profit and expenses as you plan your budget.
- If you run an e-commerce business, beware of hidden costs like shipping fees, website upgrades, and point-of-sale expenses.
- Budgeting for a startup can be especially challenging because they’re typically much more limited on data and performance history. But accurate accounting software and conservative estimates can help you improve your business budget year after year.
- If you run a service-based business, you’re working with more estimates than a product-focused business. Keep an eye on trends to make sure your budget has plenty of wiggle room.
Budgeting best practices for business
A great business budget creates a clear connection between your day-to-day operations and financial resources. It can help you navigate tough business decisions and even help you identify areas for growth. But an effective budget doesn’t happen overnight. As you create and reflect on your business budget, keep these small business budget best practices in mind:
Consider how changes impact your budget
Consider how every change in expenses or income will trickle down to your budget. Hiring a new employee doesn’t just mean you’re adding another salary but can also translate to changes in payroll taxes, benefits, and other expenses. Any time you adjust your business budget, consider the consequences.
Include all expense categories
Make sure that you’re budgeting for all expense categories, including fixed, variable, and emergency expenses. Anticipating these costs can help you balance your business budget and plan ahead. You can track your business expenses effortlessly and accurately using QuickBooks.
View your business budget as a living document
Financial circumstances change, and the unexpected happens. Your business should always be prepared to weather the storm. Review your financial statements regularly, reconsider your costs and spending, and refine your business budget as necessary.
Set goals but avoid wishful thinking
Use your bookkeeping records to determine what might transpire over the next month, quarter, or year. But ultimately, it’s a better idea to be conservative with your budget than to expect the best-case scenario.
Look out for ways to cut costs and create growth
As a business owner, it’s up to you to position your business for greatness. Break down your finances into areas of success and room for improvement. Spotting opportunities to improve your business finances can make your organization more profitable and sustainable in the long run.
Keep your money organized
Use categories or envelopes to organize your money. A business bank account that allows you to categorize or bucket your money makes it easier to stick to your budget plan and see at a glance where your finances stand. Use Envelopes in QuickBooks Money to organize your budget and hit your savings goals sooner.
What spreadsheets to keep for your small business
Spreadsheets are essential for budgeting and financial management. The following are some of the most important ones you’ll want for your small business.
Income statement
An income statement, also called a profit and loss statement, tracks your business's revenue and expenses over a specific period, such as a month, quarter, or year. It helps you understand your profitability and identify areas where you can improve your financial performance.
Cash flow statement
A cash flow statement tracks the movement of cash in and out of your business. This helps you understand your cash flow patterns, anticipate potential shortfalls, and make informed financial decisions.
Balance sheet
A balance sheet provides a snapshot of your business's financial health at a specific point in time. It shows your assets, liabilities, and equity, giving you a clear picture of your overall financial position.
Budget spreadsheet
A budget spreadsheet outlines your projected income and expenses for a specific period. It helps you plan your spending, monitor your progress, and make adjustments as needed to stay on track with your financial goals.
Free business budget templates
If you’re just getting started with budgeting for your business, these templates are a great medium for learning the process. We invite you to create copies, download, edit, and print these business budget templates.
Printable business budget template
Use this editable and printable template to create a quick and easy budget for your business:
Business budget template for Excel
Use our free Excel template to develop a budget for your business. The template uses an example budget from an imagined business, Widget Inc., to help guide you through the process of creating a business budget
How to use the Excel budget template
1. Enter prior year information
Input the year-end balance sheet and income statement into your Excel template.
Equity is the difference between assets and liabilities—the true value of your business. The $10,000 net income in the income statement increases equity in the year-end balance sheet.
2. Forecast future sales and costs
Next, we’ll make some assumptions for the upcoming year. In this example, Widget Inc.’s budget accounts for changes in sales, cost of sales, employee payroll costs, and other expenses.
Some accounting transactions, however, are unusual and cannot be included in a budget. For example, Widget Inc. had a $5,000 loss on the sale of equipment in the prior year.
Widget Inc.’s primary business is manufacturing and selling widgets, and the sale of equipment is not part of its annual budget. Accountants refer to these transactions as non-operating income and losses because day-to-day business operations don’t generate them.
3. Create a budget income statement
Widget Inc. produces a budget income statement using the assumptions in step 2. Note that the Widget Inc. budget has a line item for gain or loss on sale, other revenue. While the company may have an actual transaction in the category, this line has a zero budget.
4. Create a budgeted balance sheet using assumptions
The budgeted balance sheet includes assumptions that address each of the line items in the report. The budget provides percentage increases or decreases from the prior year, and 2 categories have no change.
5. Create a budgeted cash roll-forward for January
A cash roll-forward report lists your beginning cash balance, expected cash inflow and outflow, and your ending balance in cash for each month of the year.
The balance sheet and the income statement are financial statements, but the cash roll-forward is an informal internal report. The statement of cash flows is generated as part of your financial statements, but a cash roll-forward is more useful for budgeting purposes.
Business owners should create cash roll-forwards last because they need a cash projection for each month. Step 5 presents the cash roll-forward for January. You’ll see that the beginning of January cash balance ($10,000) is the year-end cash balance in the prior year’s balance sheet.
The majority of cash collections are from sales and the bulk of cash payments are for inventory. When a business sells inventory, the dollar amount transfers to the cost of sales, which is the largest expense in the budget. So it makes sense that the biggest cash outflow is for inventory.
Widget Inc. assumes that cash received for sales and the cash paid for inventory will be evenly distributed over 12 months. In reality, the payments will be uneven, but the cash inflows and outflows can be difficult to predict by month.
The budget also includes miscellaneous receivables collected in cash and other cash payments, such as payroll costs.
6. Budgeted cash roll-forward for February, other months
The beginning cash balance for February ($10,500) is the ending cash balance for January, and this connection applies to each month of the year. The February cash budget uses some of the same assumptions for sales and inventory purchases. The ending cash balance for February is also the March beginning cash balance.
Widget Inc. continues this same cash roll-forward process until the company has a cash budget for each month.
Business budgeting with QuickBooks
Building a business budget can feel like an overwhelming process, but it’s an essential one if you want to have an edge on the competition, maintain financial stability, and move your business forward.
QuickBooks features tools like business banking that automatically matches to your books, a business debit card integrated with your accounting software, and budget envelopes, making it easy to manage your business finances. Explore our product features to learn more.

Ken Boyd is a co-founder of AccountingEd.com and owns St. Louis Test Preparation (AccountingAccidentally.com). He provides blogs, videos, and speaking services on accounting and finance. Ken is the author of four Dummies books, including "Cost Accounting for Dummies."





