Small business owners face numerous challenges when it comes to data security, but implementing strong fraud prevention measures can go a long way toward providing peace of mind.
To facilitate unlawful transactions, scammers and bad actors may steal credit card information, PINs, and security codes. And a data breach at your small business can also lead to personal identity theft, data mining, and even a loss of control over your accounts. These threats cause large-scale harm to even the smallest enterprises and business owners.
Some might believe larger organizations are the only ones at risk for a data breach, but it also affects small businesses. In fact, according to the Association of Certified Fraud Examiners (ACFE), small businesses had the highest median loss of $150,000, compared to larger organizations.
In this article, learn how to protect your business from business fraud and what to do in the case of a security breach.
Jump to:
- Phishing and email scams
- Return and refund scams
- Money fraud
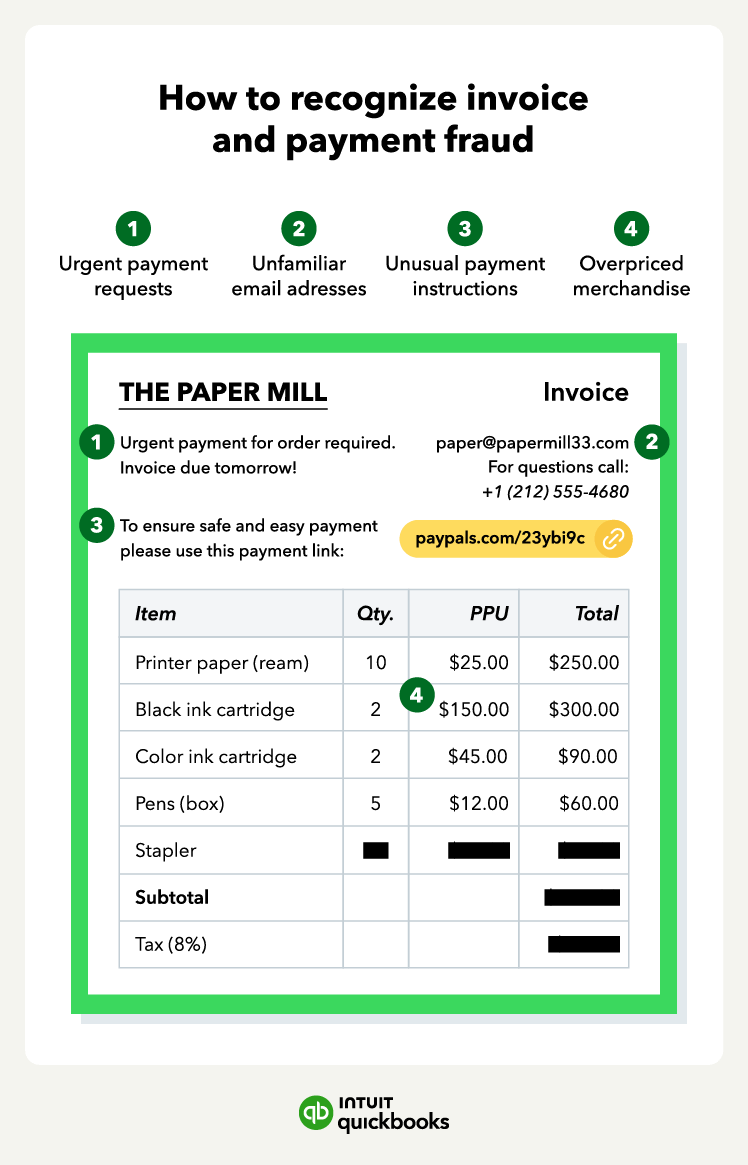
- Invoice and payment fraud
- Employee fraud
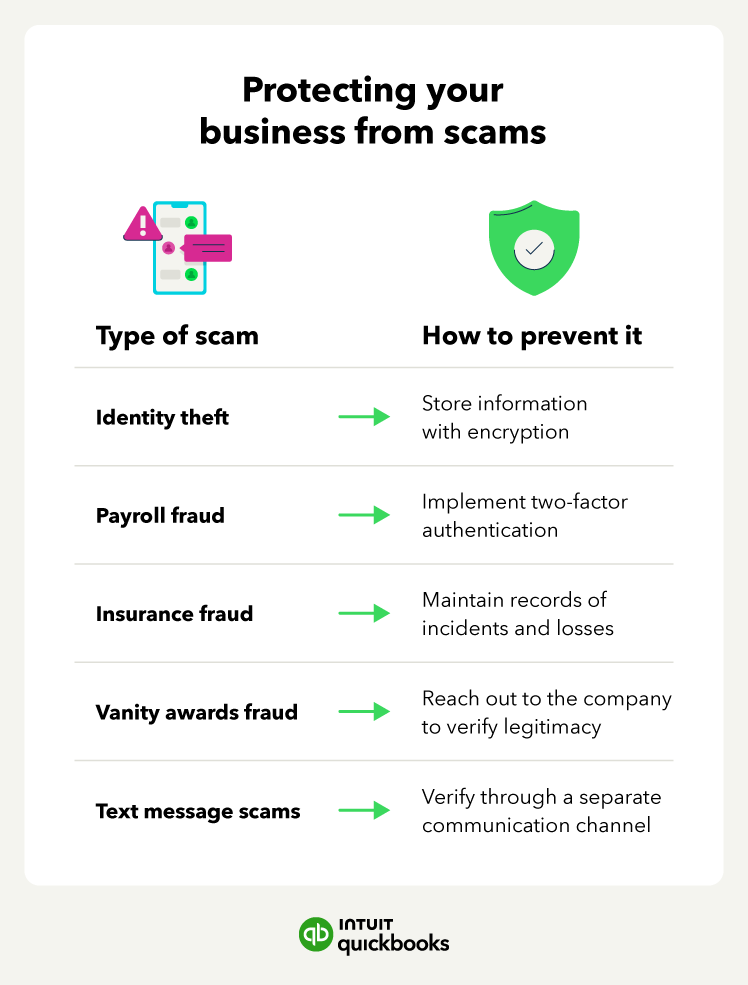
- Identity theft
- Payroll fraud
- Insurance fraud
- Vanity awards scams
- Fake text message scams
How to prevent small business fraud