Choosing the right business structure, Limited Liability Company (LLC) or S-corp, can impact your taxes, liability, and how you grow. When you first start a business, you may not think about what type of business structure you need. That usually means, by default, you become a sole proprietor.
However, a sole proprietorship isn’t a formal business entity. And because you and your business are essentially one, there’s no legal separation between the two. One option is to choose a business structure that will separate you from your business to protect your personal assets.
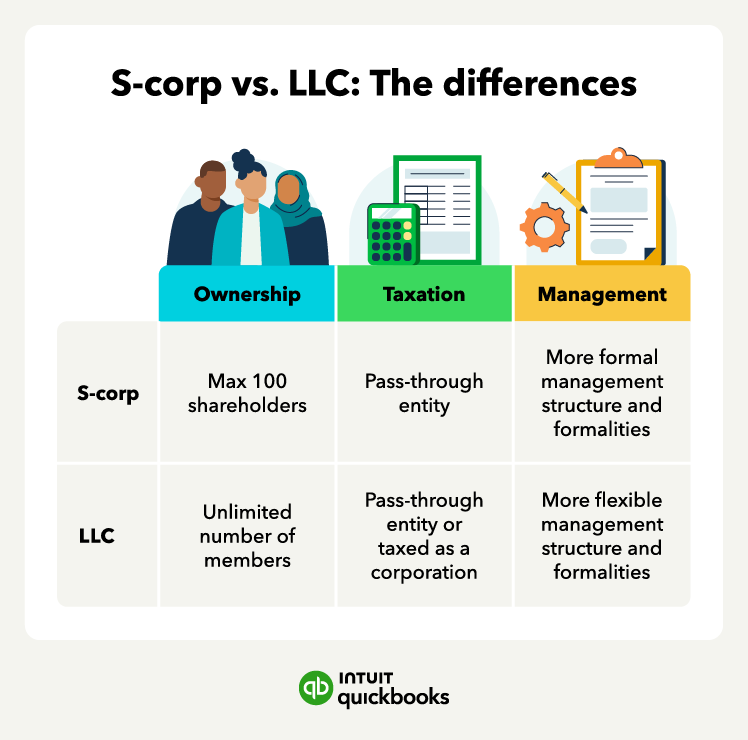
Suitable business structures to consider are an S corporation and an LLC. This guide breaks down the differences to help you decide which is best for your business.
Jump to: