Common mistakes to avoid when using W-9 and 1099 forms
Even small mistakes on W-9 or 1099 forms can lead to IRS penalties, delays, or confusion for first-time filers. Understanding where others go wrong can help you stay compliant and organized.
Not requesting a W-9 before paying a contractor
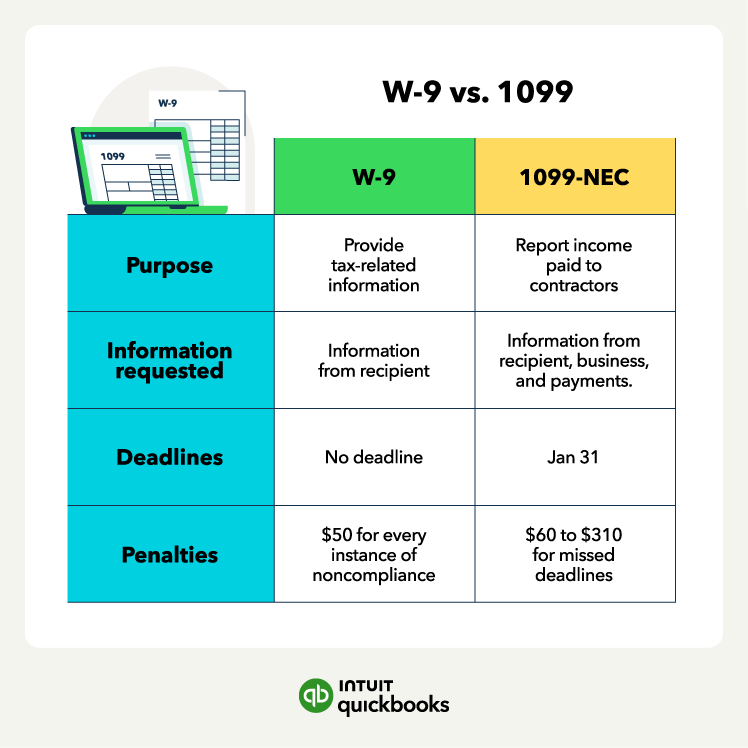
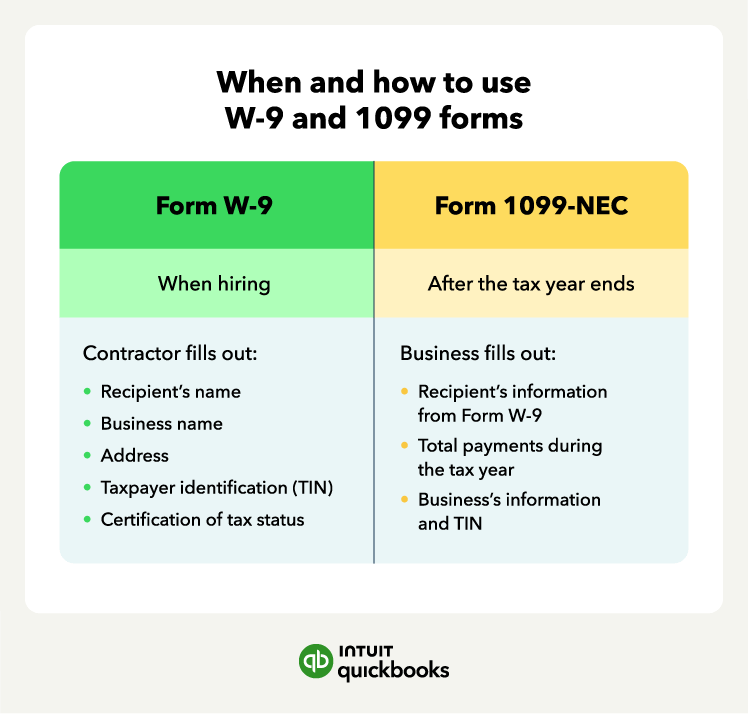
Failing to collect a W-9 before making payments is a common error. Without the contractor’s taxpayer information, you won’t have the details needed to complete a 1099 accurately.
This can lead to filing mistakes, IRS notices, and additional administrative work at year-end. You should treat W-9 collection as an essential step before issuing any payment.
Filing 1099s late or with incorrect information
Many business owners underestimate how important accuracy and timing are when filing 1099s. Common mistakes include:
- Entering the wrong TIN
- Misreporting total payments
- Missing the January 31 deadline for sending 1099s to contractors
Errors can trigger penalties ranging from $60 to $310 per form and may require corrections after the initial filing, creating extra work.
Misclassifying contractors as employees
Confusing independent contractors with employees is a frequent problem for new small business owners. Misclassification can result in incorrect tax reporting, improper payroll withholding, and legal or IRS issues. Understanding the difference, contractors handle their own taxes and work independently, while employees are on payroll, is critical to filing the correct forms.
Ignoring backup withholding requirements
When a contractor does not provide a valid TIN or gives an incorrect one, businesses may be required to withhold a percentage of their payments for the IRS. Many business owners overlook this requirement, which can create unexpected tax obligations if not addressed. Properly handling backup withholding is essential to remain compliant and avoid penalties.













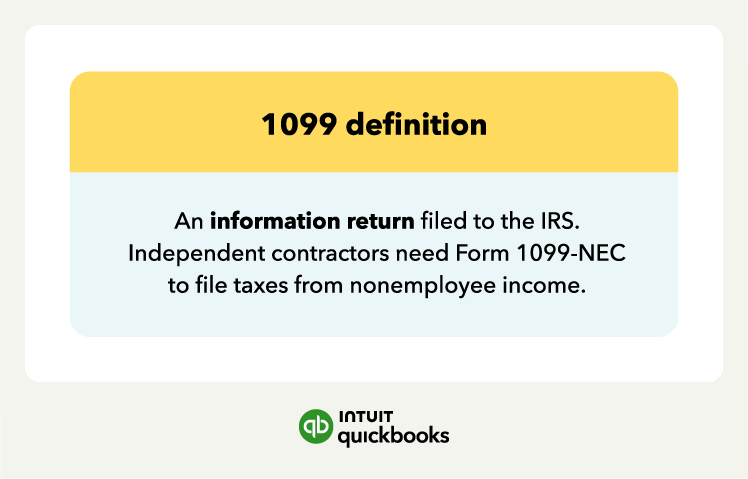
 Without a W-9, your 1099 could be rejected or flagged by the IRS, leading to fines or delays.
Without a W-9, your 1099 could be rejected or flagged by the IRS, leading to fines or delays.


