Income statement
An income statement shows a company’s revenue and expenses for a period of time. It provides information relating to returns on investments, risks, financial flexibility, and operation capabilities.
Most companies produce a multi-step income statement, which documents how a firm produces net income. In a multi-step income statement, you first find your gross profit then your operating income for a period of time.
Sales, cost of goods sold (COGS), gross profit, and operating expenses are all inputs for the income statement. So is operating income, which you generate from day-to-day business activities. Non-operating income is inconsistent and unpredictable, so you can't rely on it to produce annual profits. Your business must produce a majority of its net income from operating income activities because operating income is sustainable.
Income statement example
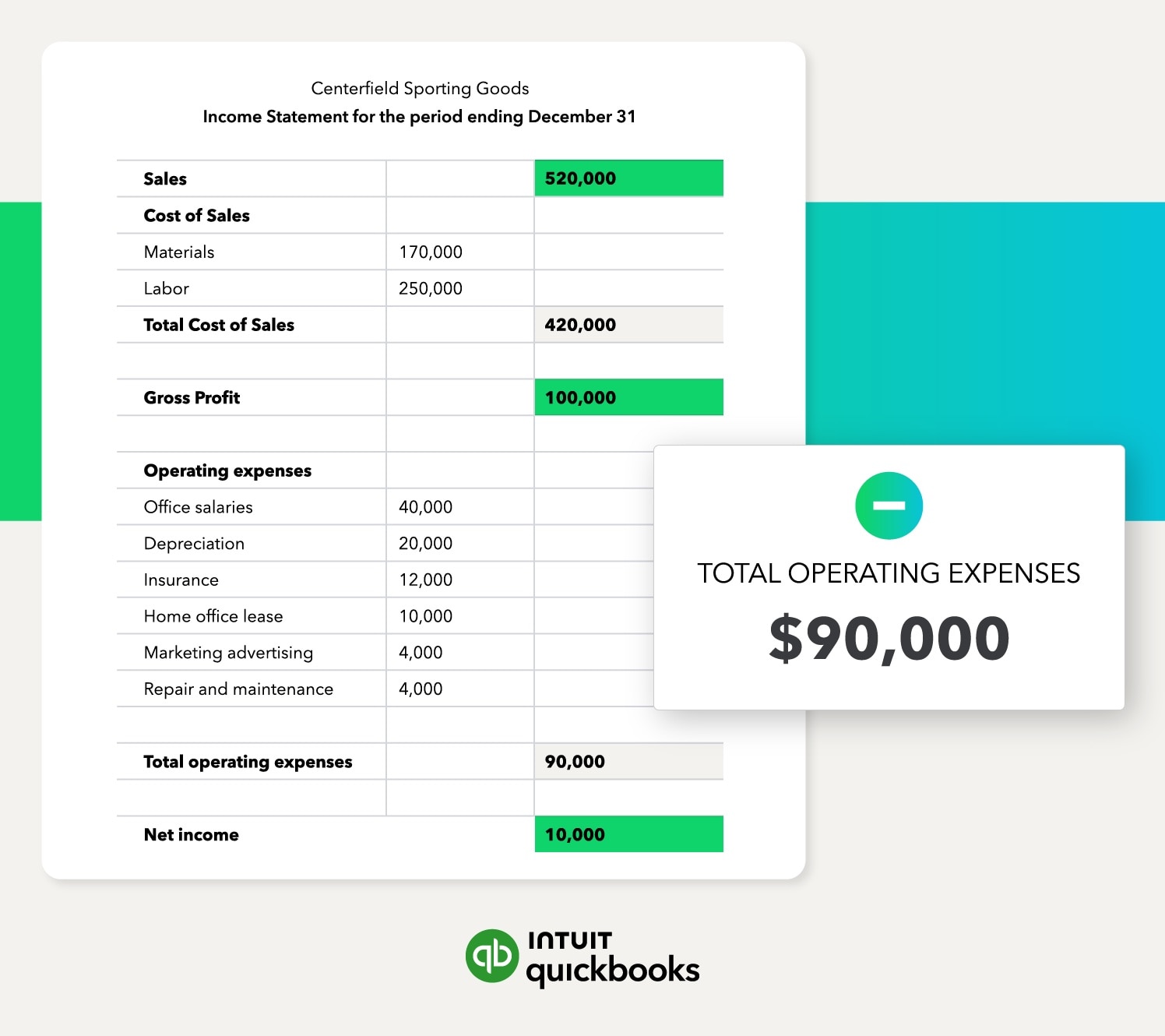
Review the Centerfield company’s income statement for the period ending December 31. Sales totaled $520,000, and the cost of sales totaled $420,000. So its gross profit was $100,000. And Centerfield had operating expenses of $90,000. That gave it $10,000 in operating income for the period. Since the company did not generate any non-operating income, its operating income was its net income balance.












.gif)