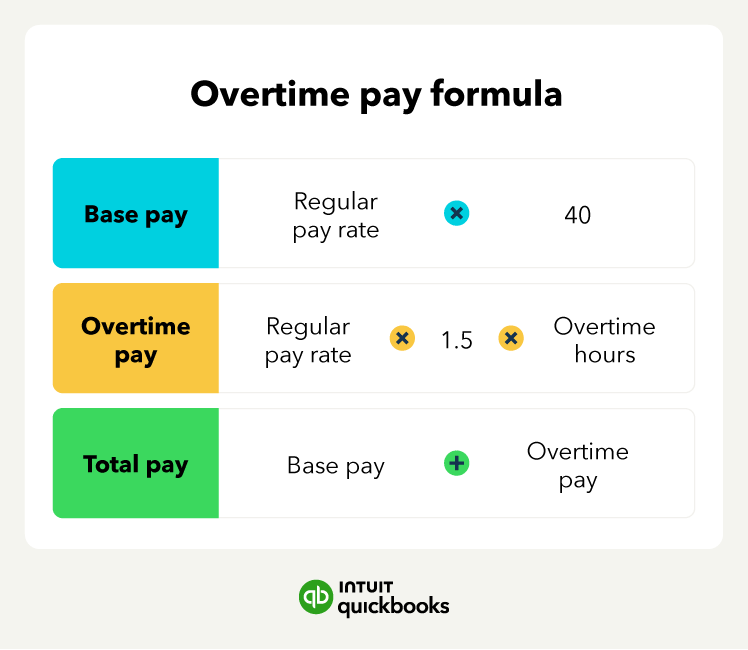
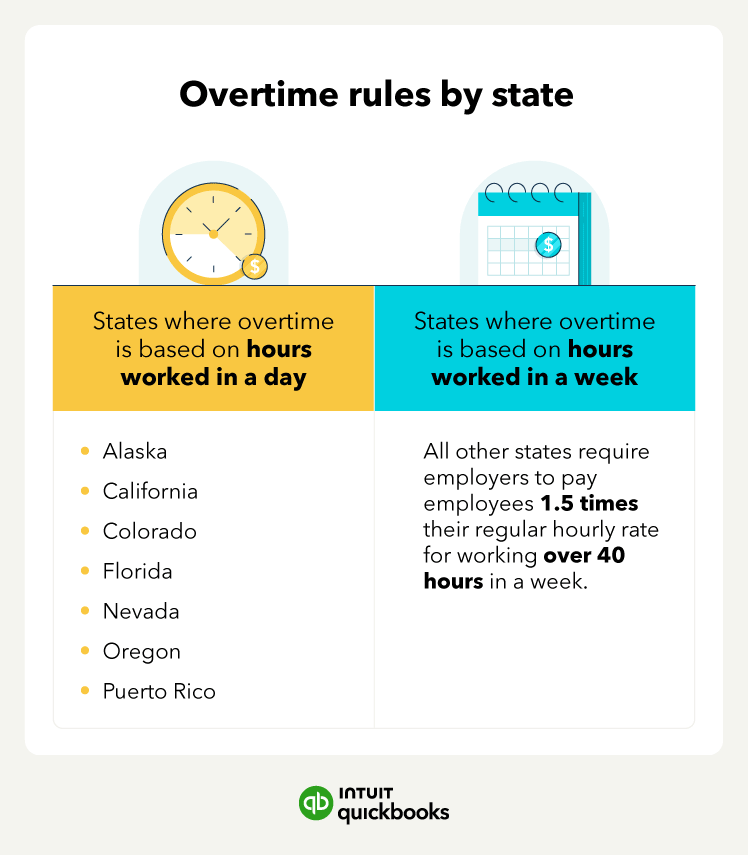
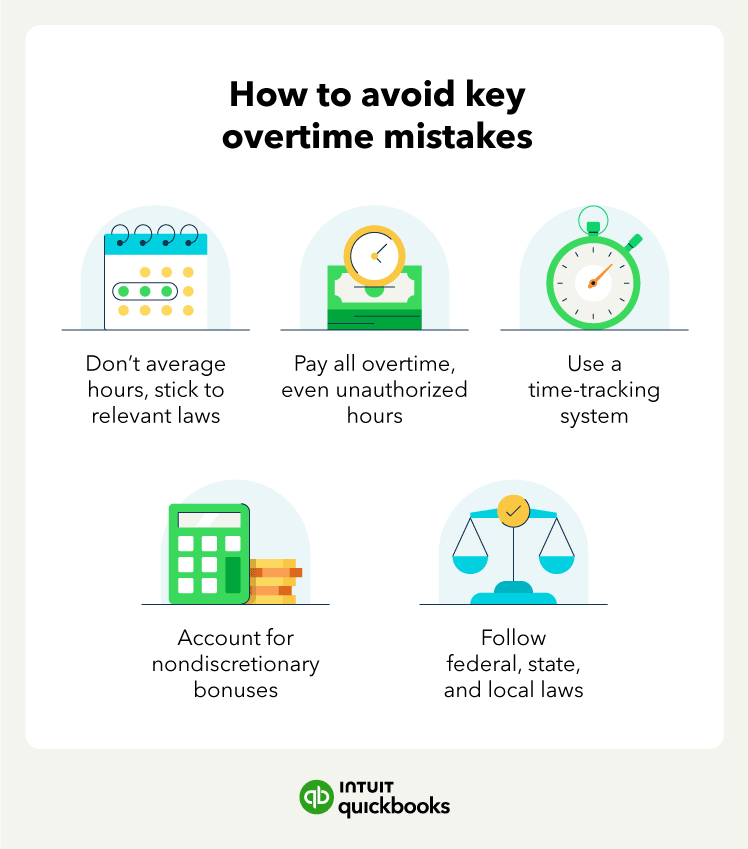
5. Calculate overtime pay for other hourly and salary employees
Beyond calculating overtime pay for your regular hourly employees, there are other cases where you’ll need to calculate and pay overtime.
For example, you may have hourly employees who also get nondiscretionary bonuses that you need to pay overtime on or a nonexempt salaried employee who works over 40 hours in a week.
Hourly employees and nondiscretionary bonus
If you offer an employee a bonus for completing a task that takes longer than their 40-hour workweek, you may owe overtime pay for the time they spent on the task.
Let’s say you have an hourly employee making $15 an hour, and they put in a 43-hour week with a $50 bonus. Below is an example of the calculation:
- Regular pay = $15 per hour x 43 hours = $645
- Total pay with bonus = $645 + $50 = $695
- Implied hourly rate with bonus = $480 / 43 hours = $16.16 per hour
- Overtime pay = $16.16 per hour x 1.5 x 3 hours = $72.72
- Total pay = $695 + $72.72 = $767.72
Hourly employees with multiple pay rates
Some employees might work different shifts with different rates of pay—or they might even have two different positions with two different rates.
To calculate this rate, you must use a blended, weighted average. Let’s say your employee worked 10 hours on two jobs in a given day—one at $10 an hour for 8 hours, then another at $12 an hour for 2 hours, and you’re in a state that uses daily overtime pay of eight hours. Here’s the calculation:
- Regular pay = ($10 x 8 hours) + ($12 x 2) = $104
- Weighted average rate = $104 / 10 hours = $10.4 per hour
- Overtime pay = $10.40 per hour x 1.5 x 2 hours = $31.20
- Total pay = $104 + $31.20 = $135.20
Salary employee overtime pay calculation
While most salary employees are exempt from overtime pay, you may still need to know how to calculate overtime pay for salary employees. That is, you can have salaried nonexempt employees that you will need to pay overtime. To pay overtime wages to these employees, divide their weekly pay by the number of hours they work in a week.
For instance, let’s say you have a nonexempt salary employee who makes $800 a week and works 40 hours a week. Their implied hourly rate is $20 ($800 / 40). If they work five hours of overtime pay during a given week, their overtime pay would be $150 ($20 x 1.5 x 5).










 Salaried workers making over $43,888 per year (effective 7/1/2024) and $58,656 (effective 1/1/2025) are not eligible for overtime pay.
Salaried workers making over $43,888 per year (effective 7/1/2024) and $58,656 (effective 1/1/2025) are not eligible for overtime pay.