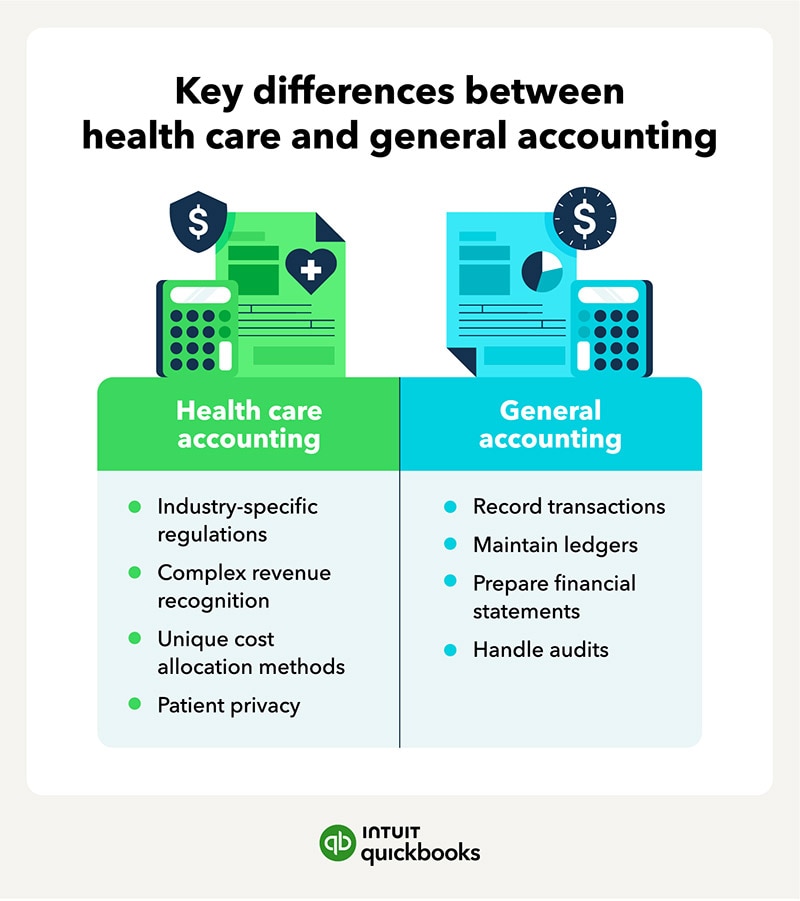
Health care accountants and accounting professionals are responsible for accurate billing, budgeting, and negotiating contracts with third-party payers. Health care and medical accounting professionals also help organizations with regulatory compliance while providing accurate financial reporting to stakeholders.
Ensuring compliance
Health care accounting professionals must be aware of any changes in federal or state regulations related to health care. They must also maintain compliance with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP).
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles are accounting standards for preparing financial statements. In the health care industry, GAAP is important, as it provides investors and stakeholders with reliable financial information.
GAAP provides a consistent method for organizations to report financial information, allowing for accurate comparisons among different entities.
Additionally, health care organizations must maintain accurate recordkeeping to comply with regulatory requirements. Proper documentation of patient information enables providers to monitor payments and medical treatments while keeping patient info private.
To abide by federal law, hospitals and other health care providers should keep comprehensive patient records.
Monitoring key expenses
Monitoring certain expenses is a key part of health care accounting. It involves tracking and analyzing health care spending across many areas. The goal of monitoring expenses is to find cost savings opportunities. This can include everything from payer contracts and supplies costs to staffing levels and equipment rentals.
One of the key steps in expense monitoring is to collect data on all relevant expenses by assessing the income statement. By identifying areas where expenses are higher than necessary, organizations can make strategic decisions about how to optimize their budget and use accounting software to manage cash flow.
Tracking depreciation
Depreciation tracking is an important part of health care accounting. This process involves tracking and recording the cost of depreciable assets over time. Depreciable assets are replaceable items such as computers, furniture, and medical equipment. By tracking depreciation costs, organizations can plan for future purchases and budget accordingly.
Depreciation tracking should begin by creating an inventory of all assets owned by the organization. This list should include purchase dates, estimated useful life, expected residual value, and other pertinent information about each item.
Health care accounting terms