Legal and ethical considerations for charging late fees
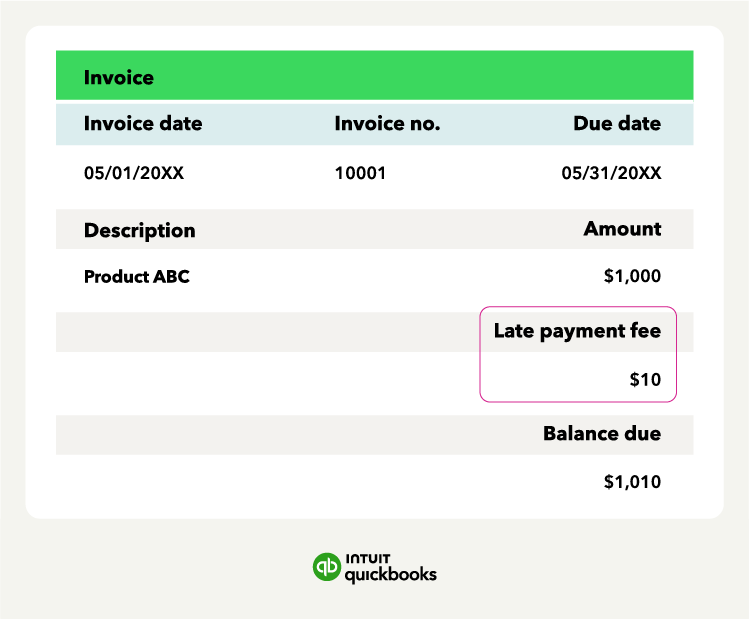
Charging late payment fees is legal in most states, but only if you follow the rules. You’ll need to be upfront about your policies, comply with any state-specific limits, and stay fair in your enforcement. Here’s what to keep in mind.
1. Disclose everything in advance
You must include your late fee policy in your original agreement or contract. If you try to charge a fee without prior notice, your customer may have legal grounds to dispute it.
2. Know your state’s limits
Some states cap the amount you can charge or require grace periods before a late fee kicks in. Always double-check local laws or speak with a legal advisor to stay compliant.
3. Avoid excessive fees
Even in states without specific limits, courts may still rule against unreasonable fees. Stick to common standards like 1% to 2% per month to avoid claims of predatory practices.
4. Be consistent, but flexible
Apply your policy consistently to avoid favoritism or legal risk, but consider offering one-time exceptions to loyal customers who usually pay on time. This helps maintain goodwill without undermining your policy.
5. Put it in writing
Any time you update your late fee terms, resend the agreement or invoice with clear documentation. Transparency helps prevent disputes and sets the tone for professional client relationships.