Compensation is a lot more than a salary. It’s the total of all the financial (and nonmonetary) benefits an employee receives from their employer. By balancing a competitive salary with desirable insurance plans, commissions, and paid time off (to name just a few possible forms of compensation), your business will have better employee retention, which will help you grow.
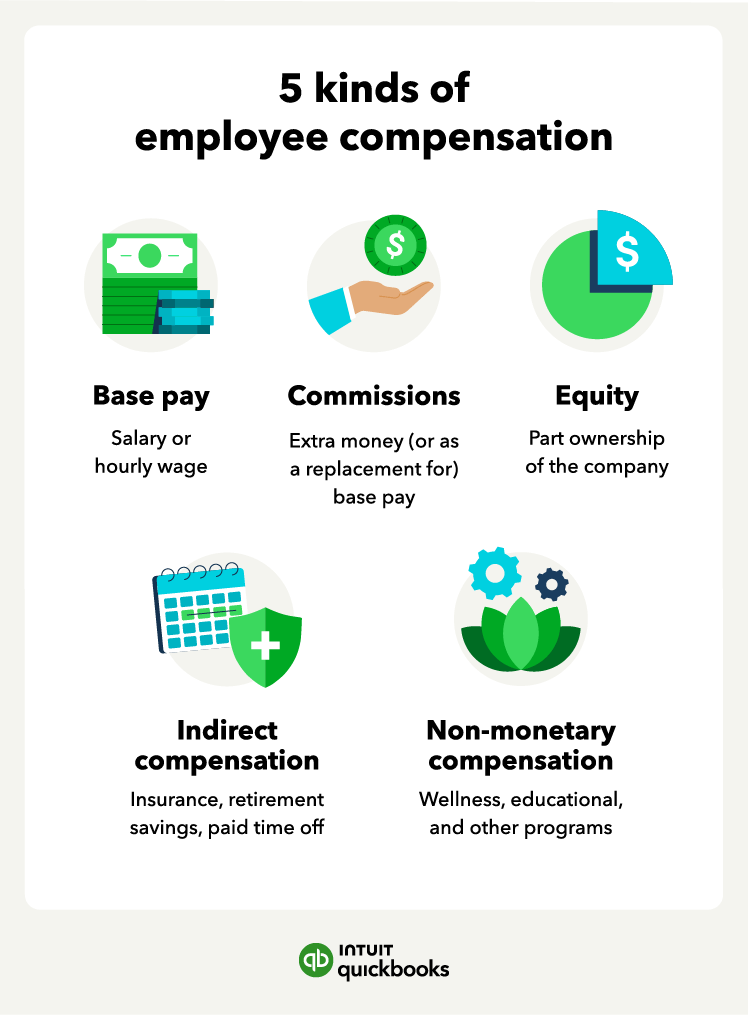
Base pay
Base pay is the amount of money that an employee is paid for doing their job. You can pay out base pay as a salary or an hourly wage. A salary is a fixed amount of pay based on a yearly total that you'll pay out regularly, while hourly wage is the amount an employee receives for each hour of work they complete. Minimum wage differs by state, so check that your company is complying with all regulations.
Base pay goes out to employees on a regular schedule, usually every two weeks or twice per month. For many people, base pay makes up the majority of their paycheck.
Base pay is taxed as earned income and is impacted by the amount the employee earns as well as any deductions they make. Base pay makes up the pool of money employees use to pay for employer-offered benefits like insurance plans and retirement savings.
Commission
Commission is a sum of money an employee earns upon completion of a specific task or duty. It's usually based on the number of sales someone makes but can also be for completing work above and beyond a certain amount. Employees can earn commission in addition to base pay, or it can be a replacement for base pay.
Commission that is a part of employees' normal paycheck are taxed at the same rate as base pay. Commission that an employee has earned separately is taxed at 25%.
Equity
Equity, also known as stock options, is a form of compensation where a company offers a percentage of ownership to employees. For startups and other young companies that can’t offer the highest or most competitive salaries, equity plans can be an attractive incentive to potential employees.
Equity plans typically have a vesting period—the amount of time an employee has to remain with the company to claim their part of the business. Create an equity pool of a certain set percentage of ownership in the company that you can divide between employees.
Owner’s equity is taxed as regular income as an employee earns shares. When they sell those shares, the employee will owe capital gains taxes.
Indirect compensation
Indirect compensation refers to the parts of a compensation plan that aren’t paid to an employee in the form of money or equity but are still valuable.
These fringe benefits (non-wage or indirect compensation perks) can include:
- Offering insurance through a company plan
- Paid time off
- Contributions to a retirement account
- Company cell phones
- Child care
- Remote work stipends
- Wellness stipends
- Education assistance
Some forms of indirect compensation are required by law if your business employs a certain number of people, while you can offer others as incentives for attracting new talent or retaining existing workers.
Health insurance and retirement account contributions are tax-advantaged payments. That means employees pay less or no taxes on them.
It’s also important to remember that not every employee will be motivated by the same forms of compensation.
Intangible/non-monetary compensation
Intangible and non-monetary compensation are some of the things that make your company an attractive place to work but don’t necessarily have a dollar value. These benefits can make up a big part of what’s commonly called “company culture.”
Some of these intangible perks include:
- Flexible schedules.
- Working from home.
- Providing time off for charity work.
- Public recognition of employee efforts.
- Social events like parties.
While some employees might appreciate expanded insurance options or other intangibles, 67% of workers said they would prefer more pay over expanded benefits.
Now that you have a better understanding of the types of compensation, let’s look at how you can build a compensation plan that will make your company the place the best people in your industry want to work.
How to create competitive employee compensation plans