Running a small business comes with plenty of uncertainties, especially when it comes to finances. You spend most of the time wondering how to plan for the future, but it’s tough to make informed decisions, secure funding, or plan for growth without a clear financial forecast. Enter pro forma financial statements.
Pro forma modeling helps you predict your financial future by estimating profits, cash flow, and expenses under different scenarios. In this article, you’ll learn what to include in these statements and how to create them so you can plan your next move with confidence.
Jump to:
- Key pro forma financial statements components
- Types of pro forma financial statements
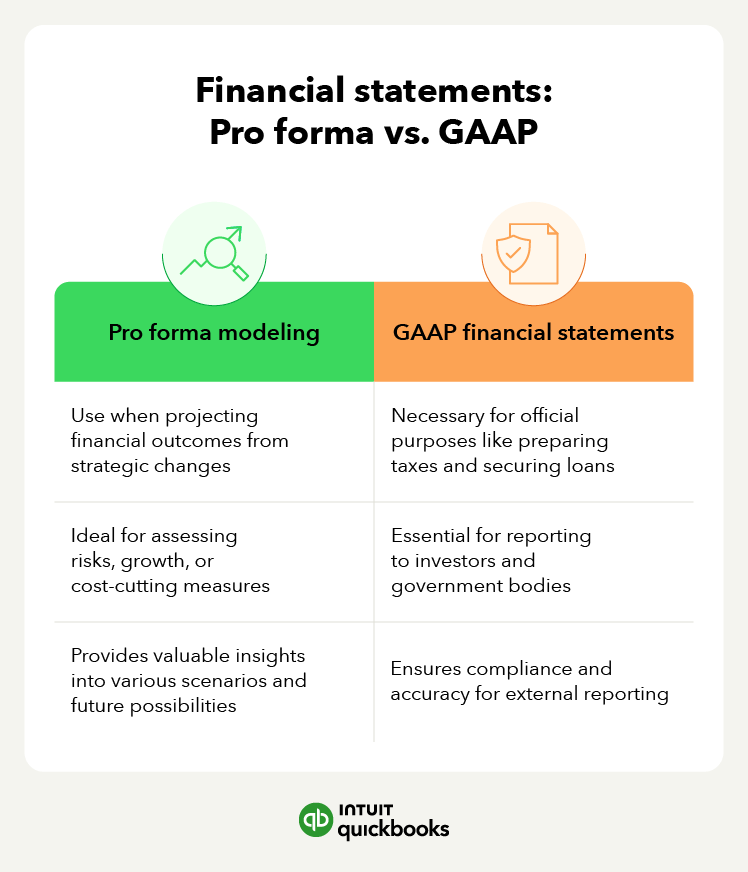
- Pro forma vs. GAAP financial statements
- Applications of pro forma financials
- How to create pro forma financial statements
- Limitations and risks of pro forma financials
- Spend more time growing your business
- Pro forma financial statements FAQ













 For accurate forecasting, prepare for variability by creating multiple scenarios and regularly update projections based on new data. Also, continuously compare your forecasts with actual performance to refine your methods.
For accurate forecasting, prepare for variability by creating multiple scenarios and regularly update projections based on new data. Also, continuously compare your forecasts with actual performance to refine your methods.