If you have a product to sell, consider the best approach to bring it to market. According to the QuickBooks Entrepreneurship in 2025 report, 37% of entrepreneurs plan to source materials differently to combat rising prices.
With this in mind, should you opt for wholesale or retail? The best choice for your business depends on various factors, from pricing and profit margins to customer relationships and market reach.
Deciding on the best business model is no light decision. In this post, we’ll cover the key distinctions between wholesale vs. retail to help you determine the most effective strategy for your business.
Wholesale vs. retail: Key differences
How to determine whether wholesale vs. retail is right for your business












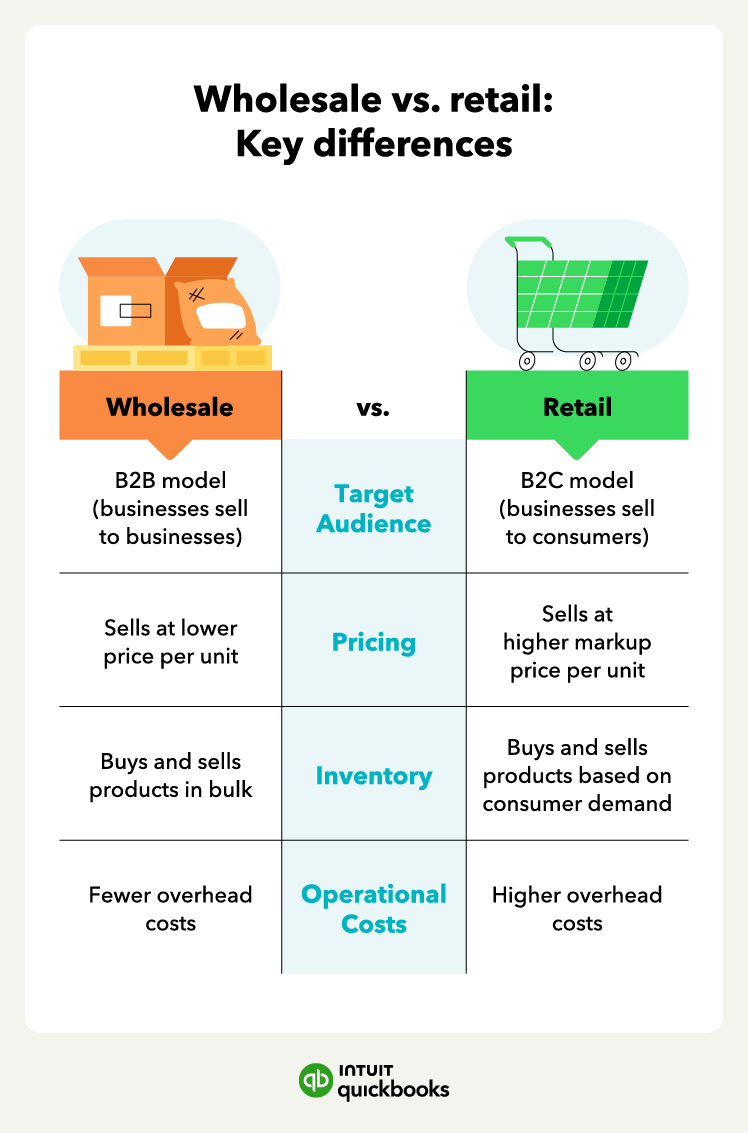
 Although wholesalers generally charge a lower price per unit for their products than retailers, they make up for it in a higher sales volume since retailers purchase wholesale products in bulk.
Although wholesalers generally charge a lower price per unit for their products than retailers, they make up for it in a higher sales volume since retailers purchase wholesale products in bulk.