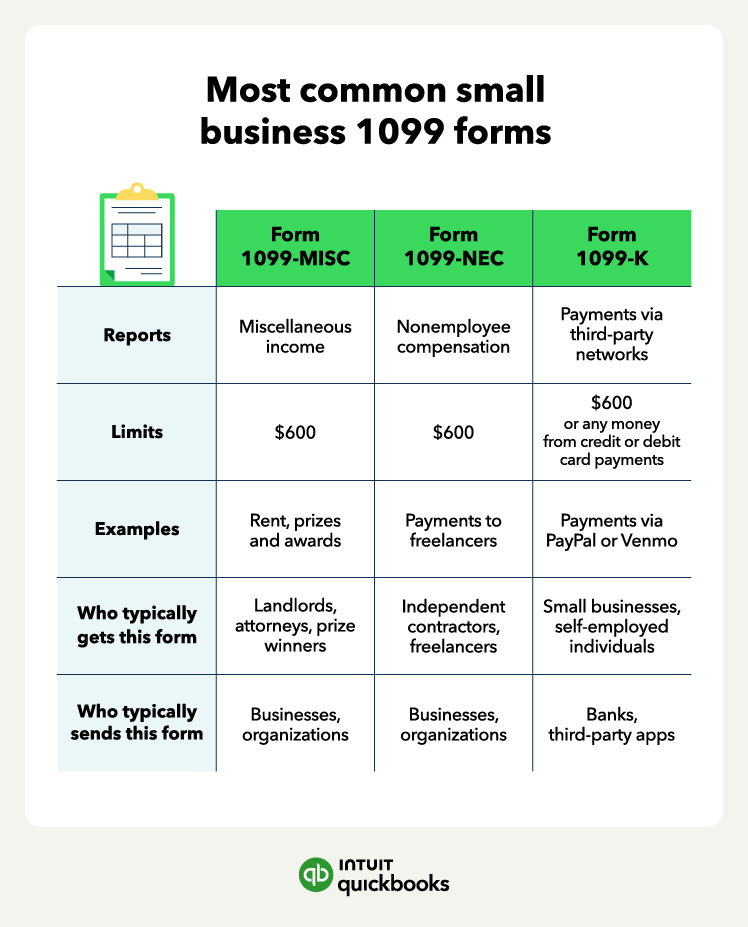
The most common types of small business 1099 forms are Form 1099-MISC, Form 1099-NEC, and Form 1099-K. Let’s break down the differences between each.
Form 1099-MISC: Miscellaneous income
Form 1099-MISC is used to report various types of miscellaneous income that don’t fall under other specific 1099 categories. Some examples include:
- Rents paid to landlords
- Prize money won in contests
- Medical and health care payments
- Payments to an attorney
- Crop insurance proceeds
- Any fishing boat proceeds
Generally, if you’ve paid someone $600 or more in any of these categories, you need to file a 1099-MISC for them. Individuals or businesses receiving miscellaneous income payments typically get this form, while businesses or entities making these payments send it. This form is also used if you sold $5,000 or more of consumer products directly to someone who plans to resell them, and the sale didn’t happen in a permanent store.
Form 1099-NEC: Nonemployee compensation
Form 1099-NEC specifically deals with payments made to independent contractors or freelancers for services rendered. If you're a freelancer or independent contractor, this is a form you should receive if you've earned $600 or more from a single client during the year. If you’ve hired someone who isn't your employee and paid them at least $600 for their work, you'll likely need to provide them with a 1099-NEC.
This form ensures that both the contractor and the IRS are aware of this income, which is subject to self-employment taxes.
Form 1099-K: Payment card and third-party network transactions
Form 1099-K reports payments received through electronic means and from credit, debit, or stored-value cards. For example, credit card sales on an online marketplace like Etsy or payments for services via PayPal or Venmo.
As of 2023, the reporting threshold is $600 in gross payments, regardless of the number of individual transactions. Payment processors typically send this form to both the recipient and the IRS, ensuring transparency in increasingly common digital transactions.
Note: You must file an income tax if you earn $400 or more from self-employment. Your Form 1040 is different from your 1099 forms. Your 1040 form is the individual income tax form both employees and independent contractors use.