Credit and debit cards
Payment method that can come with higher processing fees relative to other e-payment solutions.
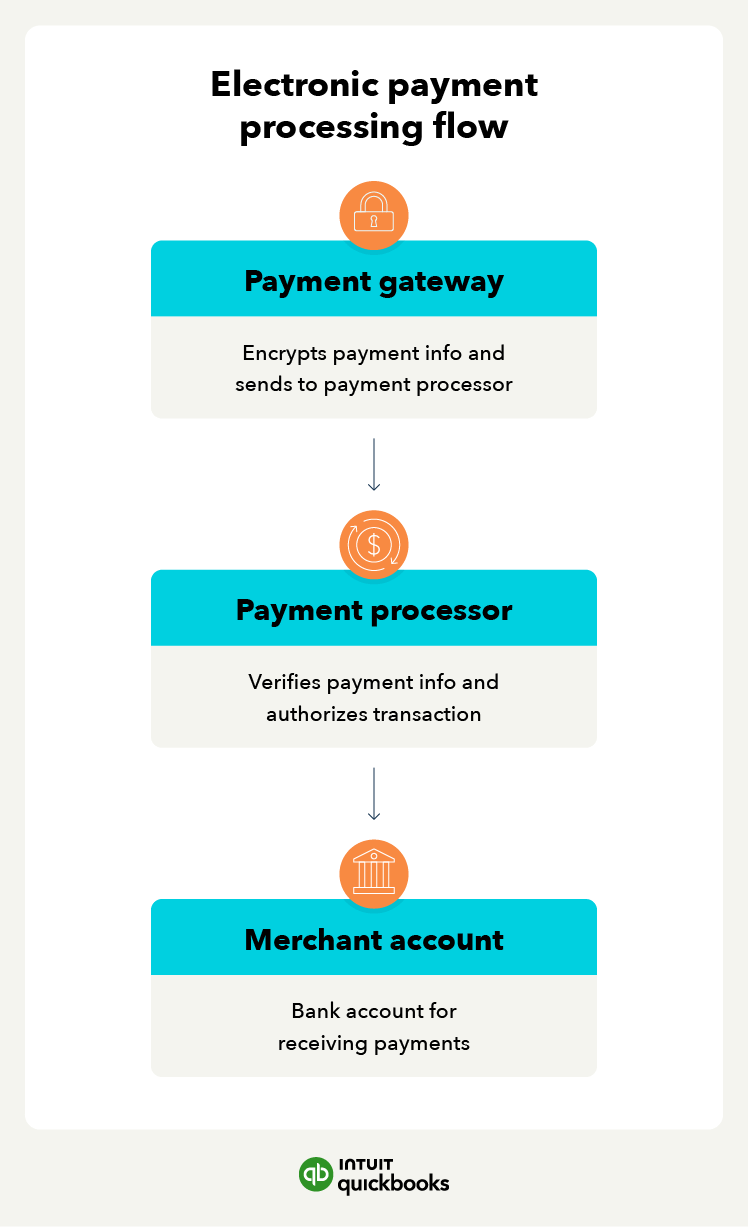
Credit and debit cards are two common types of electronic payments that offer convenience and security for financial transactions. For these payments, payment details are entered manually during checkout, or the physical card is processed at a point-of-sale (POS) system.
There’s usually a debit or credit card processing fee, which the seller needs to pay. Fees are typically a percentage of the transaction.
Bank transfers
Direct bank-to-bank payments, often used for larger or international transactions, known for speed and security but typically have higher fees.
Bank transfers, commonly referred to as wire transfers, represent a method of electronically moving funds directly from one bank account to another. These are often utilized for transactions requiring a high degree of security, speed, or for transferring larger sums of money, including international payments.
To execute a wire transfer, the sender instructs their bank to send funds directly to the recipient's bank account. This requires specific information, such as the recipient's bank name, account number, and routing number for domestic transfers.
For international transfers, details like a SWIFT code or IBAN are typically necessary. The transfer usually occurs through secure bank networks like Fedwire (in the U.S.) or the SWIFT network for international transactions. Domestic wire transfers can often be processed within the same business day, while international wires may take longer.
Compared to other electronic payment methods like ACH, wire transfers are generally faster but come with significantly higher transaction fees, often charged to both the sender and sometimes the recipient. Due to the cost and process, they are less common for everyday small business sales but are prevalent in B2B transactions, real estate, and sending money abroad.
ACH transfers
Payments are simple and convenient once you link accounts, but many banks have limits on the amount you can send through this method.
ACH transfers, also known as online banking payments, are another common form of electronic payment. With an ACH transfer, money moves directly from one bank account to another using a centralized system called the ACH network. For example, if your employees have direct deposit, that’s a form of ACH transfer—the money moves from your business account to your employees’ accounts.
To initiate an ACH transfer, the sender provides their bank with the recipient's bank account information. The sender's bank then communicates with the ACH network to electronically move the funds from the sender's account to the recipient's account. This process typically takes a couple of days.
Note that there is a fee for processing ACH payments, but it’s typically cheaper than credit or debit card processing fees. These fees are typically either a flat fee per transaction, a percentage fee, a monthly fee, or a batch fee. The fees are generally lower than those for card payments, however.