It is important to note that each country has specific commercial invoice requirements, including required forms and additional documentation. To avoid delays, check official sources in the destination country to ensure compliance.
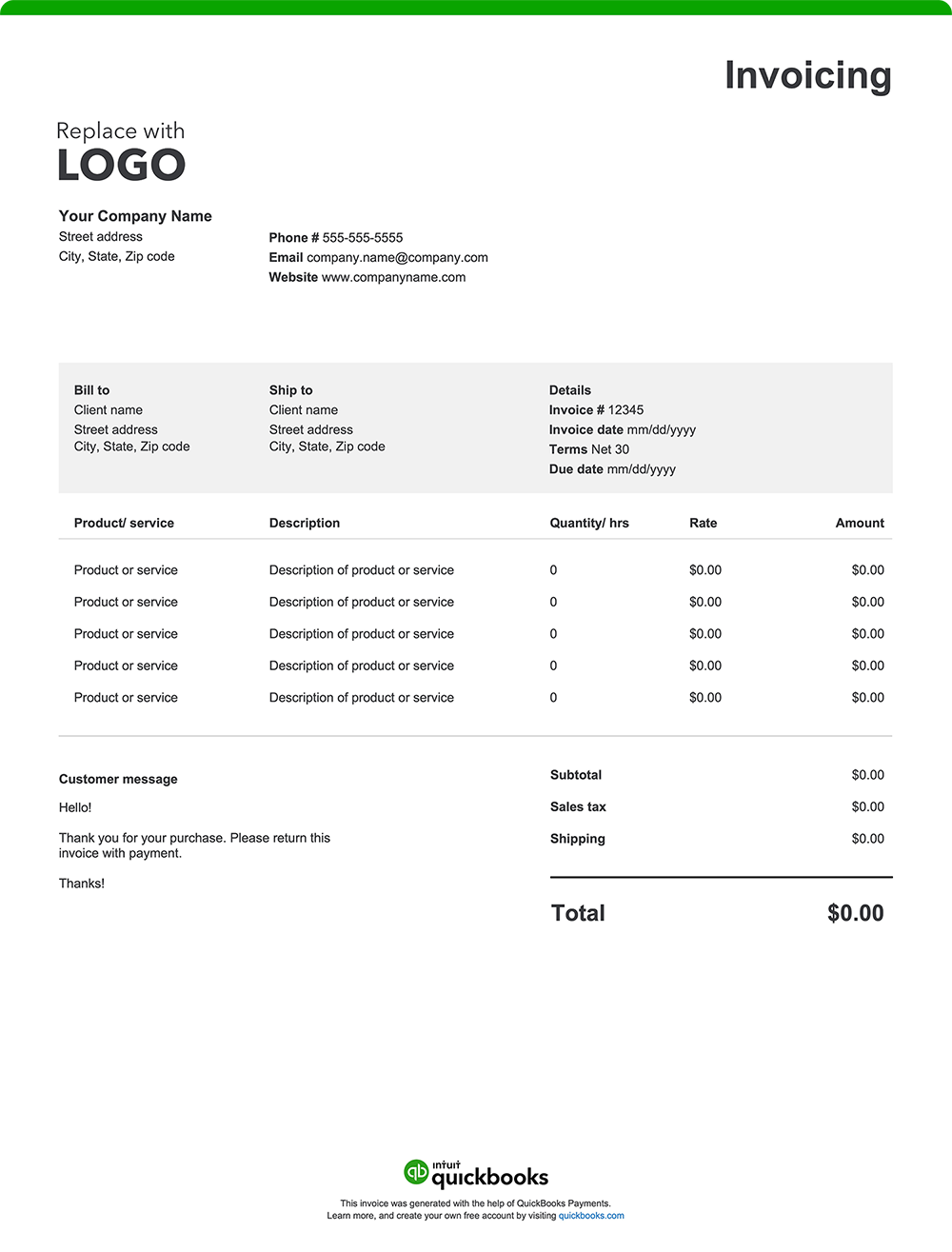
A well-structured commercial invoice provides transparency, prevents delays, and keeps your business's international shipment and trade operations running efficiently. While formats and specific requirements can vary by country of import, here are 14 essential elements every commercial invoice should include:
1. Exporter/seller information
Your invoice should include your company name, address, and contact information. Identifying your exporter details ensures that customs authorities and your buyer can verify the origin of the goods and contact you if necessary.
2. Buyer/consignee information
Include the receiver’s company’s name and contact information. This information is necessary for proper delivery and for customs authorities to determine the final destination of the goods.
3. Invoice number
A unique invoice number aids in tracking and referencing the transaction, facilitating efficient recordkeeping and communication between parties.
4. Date
The invoice date establishes the timeline for payment terms and is essential for financial records and compliance with contractual agreements.
5. Description of goods
Provide detailed descriptions of your goods, including the quantities, unit prices, and total value. Customs authorities rely on this information to classify products accurately, which determines the applicable duties, taxes, and import fees.
6. Harmonized System (HS) code
The Harmonized System code is a globally recognized classification system used to categorize goods for international trade. This code is required on every commercial invoice to ensure customs authorities can accurately assess duties and taxes. Without the correct HS code, shipments may be delayed, misclassified, or held at customs.
7. Country of origin
Your commercial invoice must specify where the goods were manufactured or produced in order to apply correct tariffs, adhere to trade agreements, and enforce import restrictions or quotas.
8. Total invoice value
Include the total value of all the shipment contents. This value is used by customs to assess duties and taxes and serves as a record of the transaction's financial value.
9. Currency of transaction
Specifying the currency ensures clarity in payment terms and prevents misunderstandings regarding the amounts due.
10: Mode of shipment
Indicate whether the shipment is by air, sea, or land. This information can be used to track goods, estimate delivery times, and determine applicable shipping regulations.
11. Freight and other charges
Provide transparency and support accurate duty and tax assessments by itemizing costs related to shipping, insurance, and any other additional fees.
12. Payment terms and instructions
Your invoice should include straightforward payment terms and instructions that outline exactly how and when you expect to be paid. Be sure it lists the following:
- Payment timeframe: Specify the timeframe for payment, such as "Net 30" (payment due within 30 days of the invoice date), "Due on Receipt," or any other agreed-upon terms.
- Accepted payment method: List the payment types you accept, such as credit cards, online payment platforms, wire transfers, or Letters of Credit.
- Payment details: Include all required information for each payment method, like your check mailing address or online payment portal link.
- Late payment penalties: If you charge penalties for late payments, state the penalty amount or percentage.
- Early payment discount: Mention any discount available for early payment and eligibility criteria.
13: Certification statement
A certification statement is a declaration confirming the accuracy and authenticity of the information on the invoice. It should be signed by an authorized individual.
14: Destination Control Statement (DCS)
The Destination Control Statement (DCS) is mandatory for U.S. exports that require a license under the Export Administration Regulations (EAR) or International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR). It must be included on the commercial invoice to confirm that the shipment is only authorized for the specified country and recipient, preventing unauthorized resale or transfer without U.S. government approval.
How do I send a commercial invoice?
You will submit a commercial invoice with your shipment, as it’s required for customs clearance. Typically, two copies are attached to the outside of the package for customs officials, and one copy is kept by you, the exporter, for your records. The consignee also receives a copy, often included inside the package. Governments use the commercial invoice to determine the true value of goods when assessing customs duties and taxes.
Risks of an incomplete or inaccurate commercial invoice
An incorrect or incomplete commercial invoice can lead to shipment delays, increased scrutiny, and potential legal or financial penalties from customs authorities. Inaccuracies can also disrupt supply chains, affect customer satisfaction, and result in additional costs to correct the problem. So, it is important that businesses take extra care when preparing commercial invoices, ensuring all required information is accurate and complete before shipment.