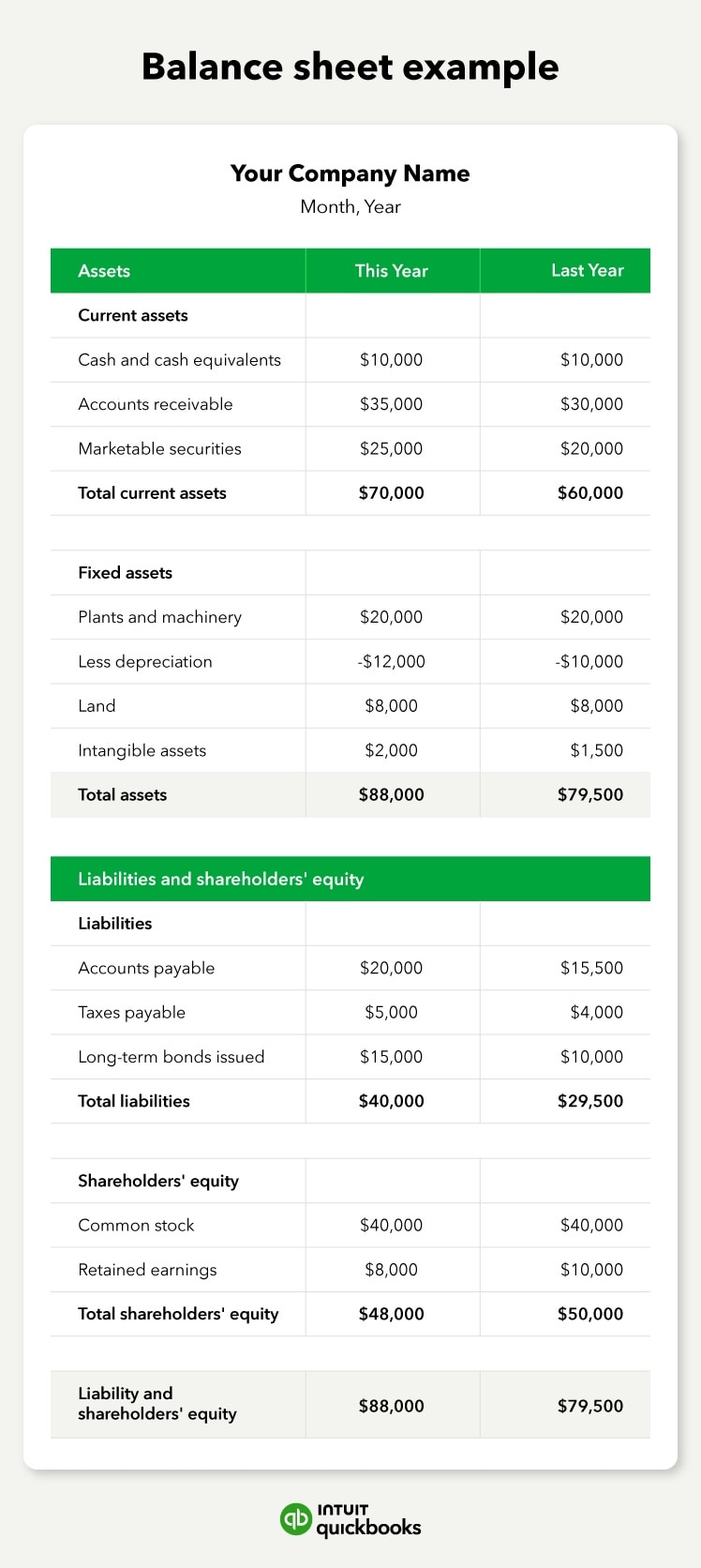
With the accounting equation, you can better manage your business’s finances and evaluate your business transactions to determine whether they’re accurately reported. If both ledgers of your balance sheet don’t match, there may be an error.
Accounting basics for small businesses
As a small business owner, you need to understand a few key accounting basics to ensure your company operates smoothly. Below, we’ll cover several accounting terms and principles you should have a firm grasp on. For a complete list, refer to our full lists of accounting terms and accounting principles.
Accrual basis accounting method
The accrual basis accounting method recognizes expenses and revenues at the time of a sale.
Cash basis accounting method
The cash basis accounting method recognizes expenses and revenues when a payment is received.
Accounts receivable
Accounts receivable is money owed by customers for a product or service they purchased.
Income statement
The income statement is a financial document that summarizes a business’s income, expenses, and total costs over a specific period to determine its profits or losses.
Cash flow statement
The cash flow statement is a financial document that shows the money coming in and going out of your business accounts.
Generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP)
GAAP is a global standard for financial reporting with a wide array of principles, such as how to recognize expenses and assets, liabilities, and revenue, how to measure and report profits and losses, and how to present information on financial statements.
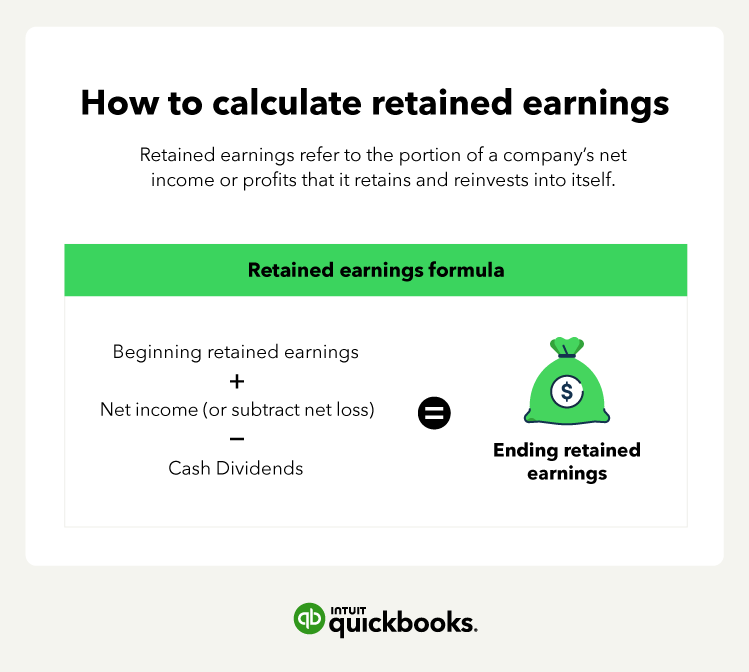
Using accounting formulas to monitor your company’s financial health
A thorough accounting system and a well-maintained general ledger help accurately assess your company’s financial health. There are many more formulas that you can use, but the 11 we covered in this article are undoubtedly key for a profitable business.
Although these equations seem straightforward, they can become more complicated in reality. Many small business owners find it much more challenging to balance the right side of the equation with the left side when factoring in the potentially hundreds of accounts they have in their company.
Fortunately, you don’t have to worry about it, as accounting software can help. All you need to do is enter your business transactions. Your accounting software will then crunch the numbers so that you can analyze your business’s health.